
Vermicomposting
- Lesson
- Grades K – 2
Students create a worm bin which will serve as a basis for investigations about ecosystems, life and nutrient cycles, and decomposition.
Standards-based resources for teaching through the lens of agriculture.

Students create a worm bin which will serve as a basis for investigations about ecosystems, life and nutrient cycles, and decomposition.

Students investigate soil texture and determine the texture of several soil samples.
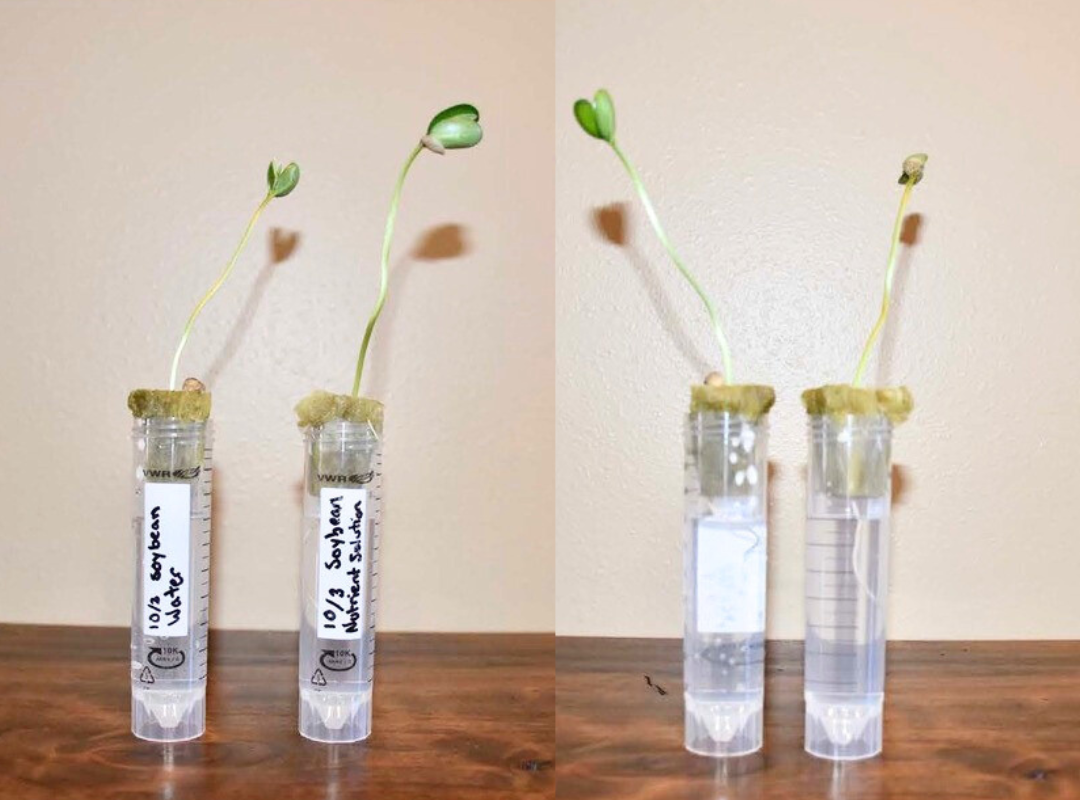

Investigate the importance of nutrients to support plant growth and discover how plants grow without soil by growing and observing plants in a test tube hydroponic system.
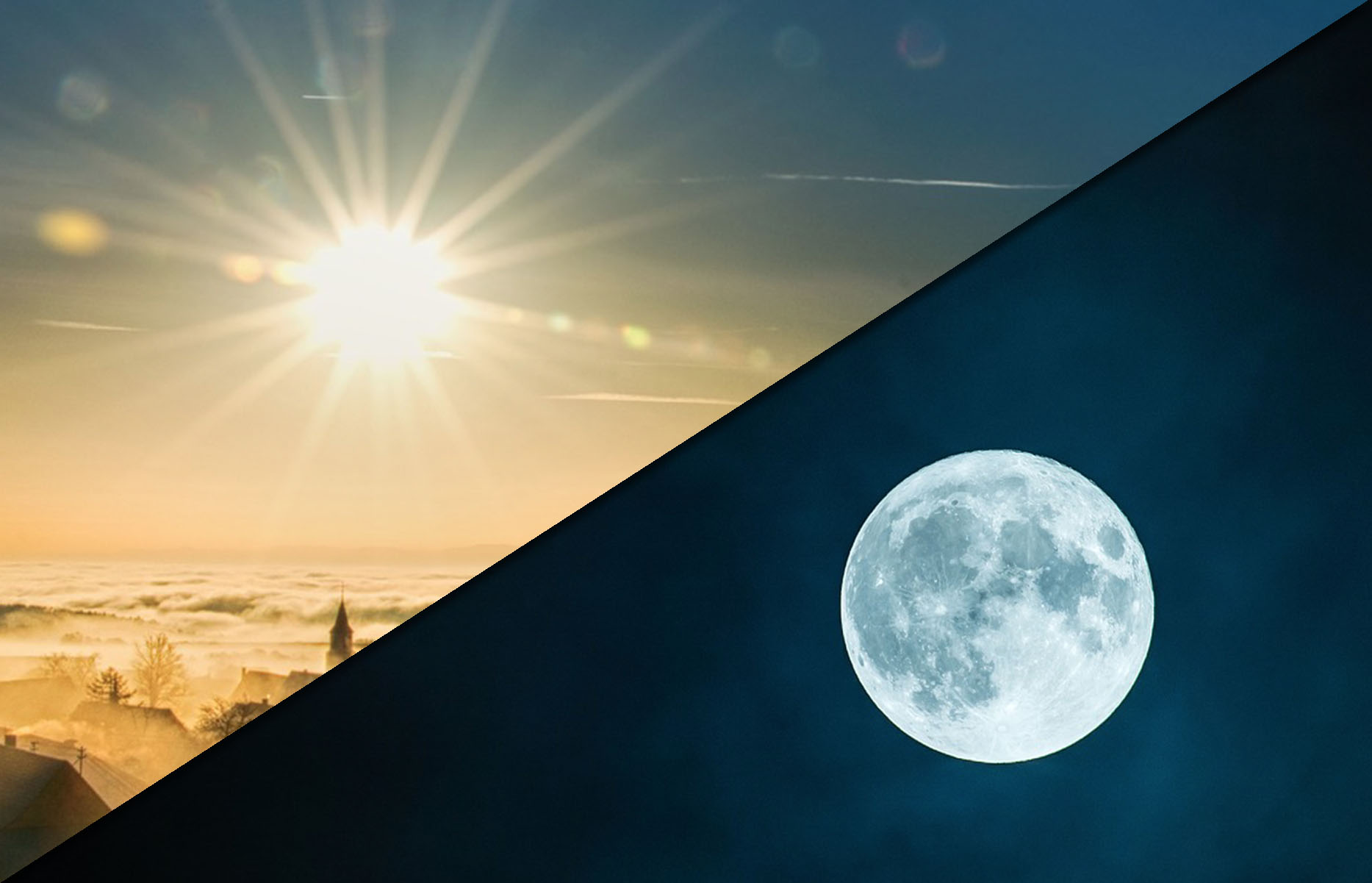

Students will understand how photoperiodism impacts plants and animals in the environment and learn how egg farms use this science to manage the laying of eggs by their hens.

This is a great kit for teaching students about soil textures. The kit includes two cups of sand, two cups of silt, and two cups clay. All of the soil samples are from the state of Utah and are representative of the Intermountain Region, although the mineral content may be different, the particle sizes are true to soil texture type and can be used by other states for demonstration purposes. Order this kit online from agclassroomstore.com.

From apple cores to zinnia heads, readers will discover the best ingredients for a successful compost pile. How do you start a compost pile? What's safe to include? This book provides the answers.

Students explore the process of making wool into cloth.

Students explore different cultures around the world and their unique traditions centered around food and its preparations. Students discover how food gets from the farm to the grocery store.

Students identify the structure and function of six plant parts and classify fruits and vegetables according to which parts of the plants are edible.

Students investigate six major livestock species, discover that animals need air, space, food, water, and shelter to survive, explore the life cycle of a farm animal, and identify the products each farm animal produces.

Students identify the characteristics of the four seasons of the year, investigate what causes seasons, and observe the effects changing seasons have on farms.

Students identify different breeds of chickens, examine physical characteristics, and determine the stages of a chicken's life cycle.
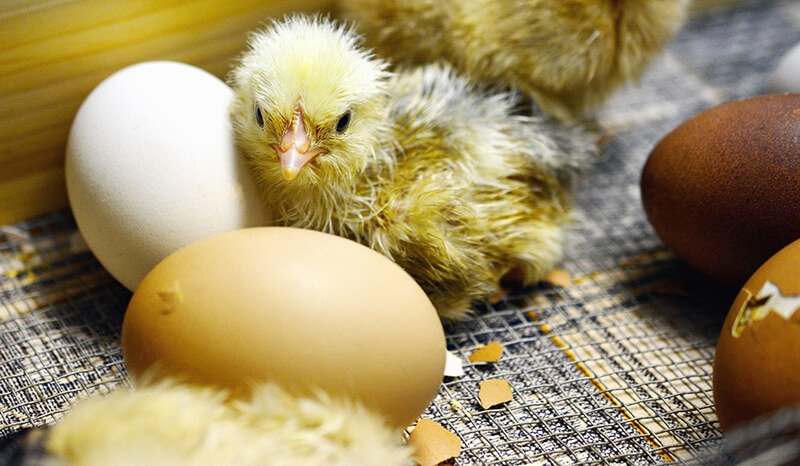

Students explore how an embryo develops inside of a chicken egg over time, discuss life cycles and other natural cycles, and observe similarities and differences between parents and offspring.
Students discover the needs of a seed to germinate and the needs of a plant to grow while exploring the life stages of a flowering plant.
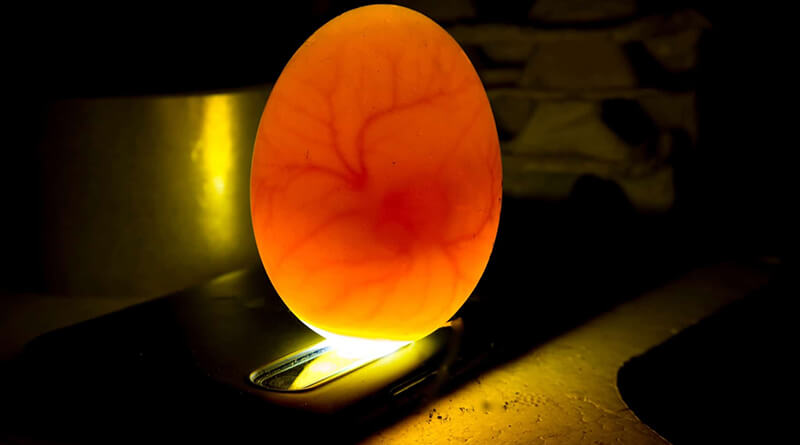

Students investigate embryo development in chicken eggs.
Students use the visual representation of a web to explore the role of agriculture in their daily lives and understand how most of the necessities of life can be traced back to the farm.
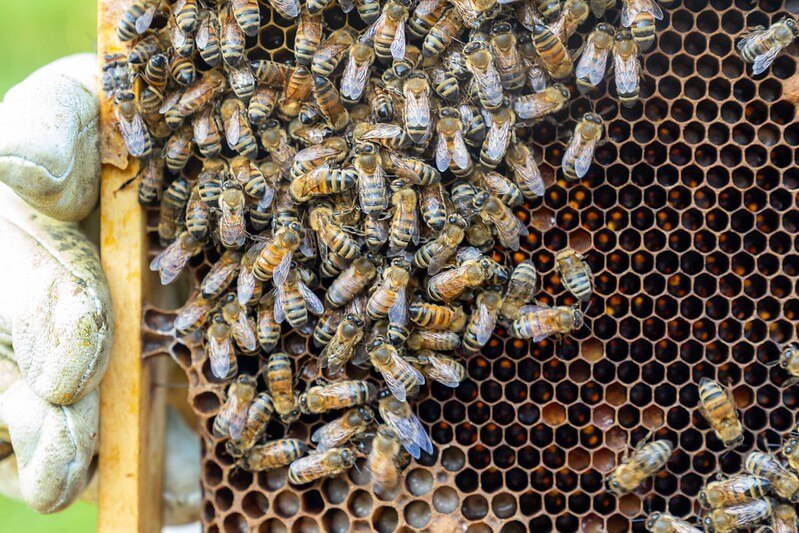

Students investigate the three types of honey bees in a colony, identify their roles, and recognize honey bees as part of a community that works together.
Students explore appropriate serving sizes and determine how to make healthy dietary decisions by identifying the components of nutrition as illustrated by MyPlate.

Students explore the wide scope of agriculture, identify the variety of agricultural products and by-products they use in their daily lives, and discuss the difference between needs and wants.
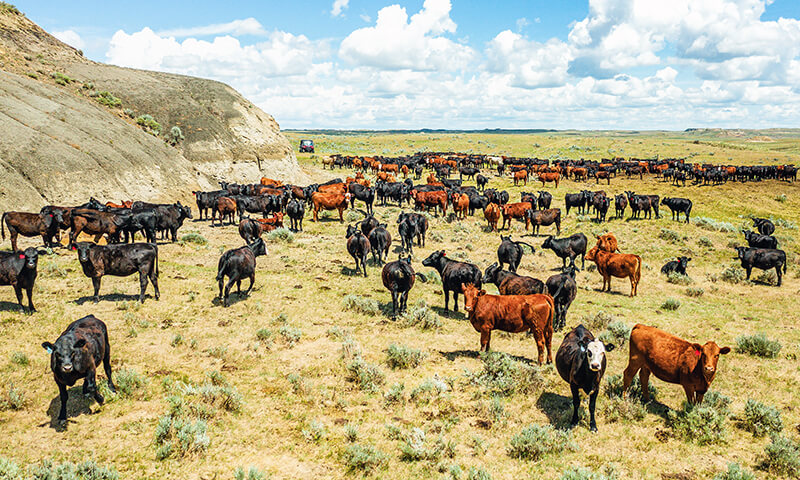

Students explain the value of the beef cattle industry, including the products cattle produce, the production process from farm to plate, and how cattle can utilize and obtain energy from grass and other forage.

Students examine the growth, composition, history, and uses of corn through a close reading activity, discussion of renewable and non-renewable resources, and hands-on exploration of bioplastics made from corn.

Students explore different cultures around the world, compare worldwide communities with local communities, and explain the interrelationship between the environment and community development.
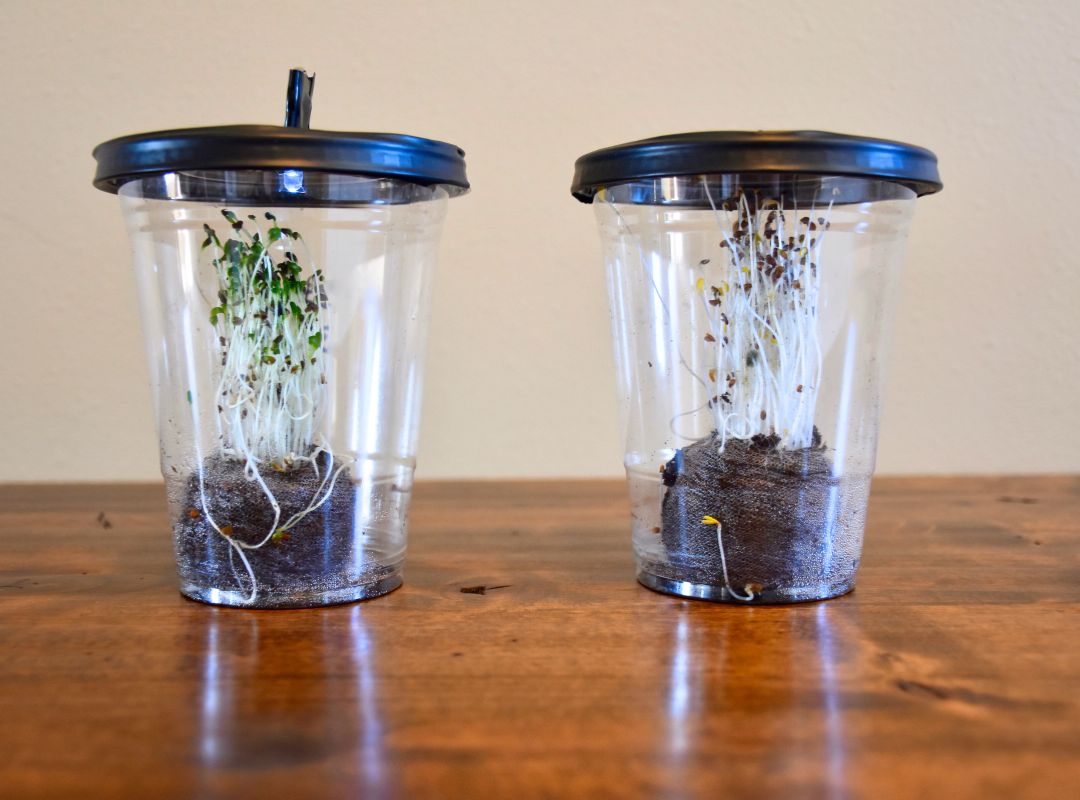

Students investigate the importance of light to plants by creating a desktop greenhouse investigation and exploring the process of photosynthesis.

Students identify different breeds of chickens, examine physical characteristics, and determine the stages of a chicken's life cycle.
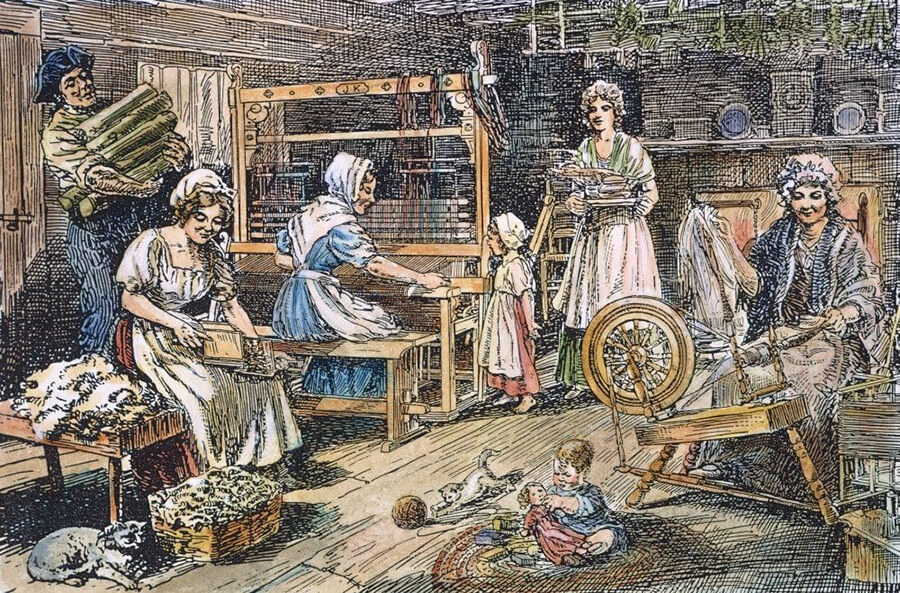

Students investigate how the need for wool impacted the American colonists by examining the Wool Act of 1699, determine the importance of wool in colonial America, and compare and contrast the differences between processing wool then and now. Students spin, weave, and dye wool to explore how wool was processed in Colonial times.
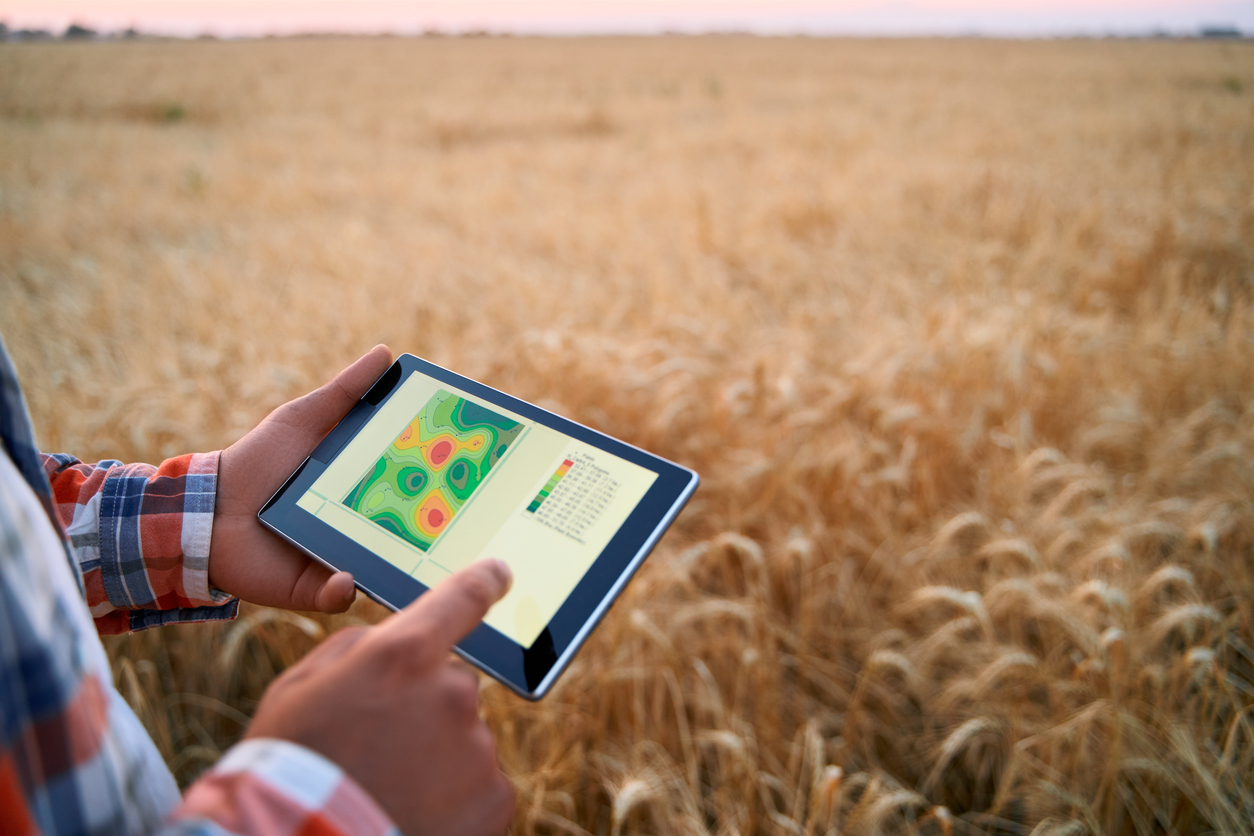

Students discover technologies that are used on farms to increase efficiency and yields and decrease costs and environmental impact.
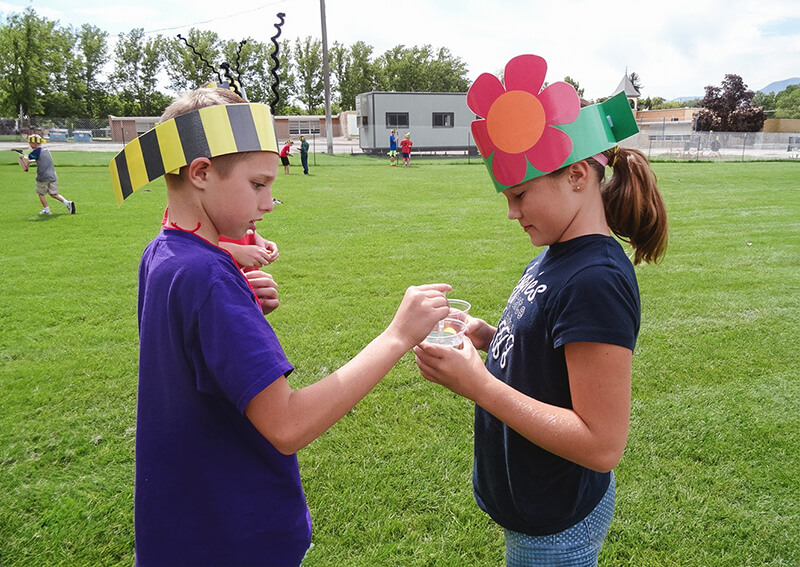

Students identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination.

Students compare the differences between natural and managed ecosystems and describe ways in which farmers can protect agricultural ecosystems.
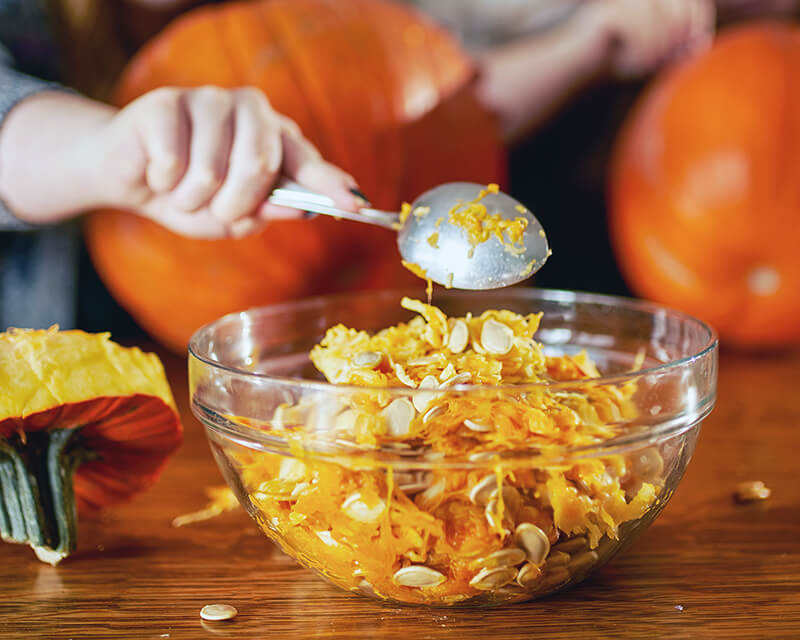

Students estimate the size and weight of pumpkins, sprout pumpkin seeds, and make pumpkin pie in a bag.
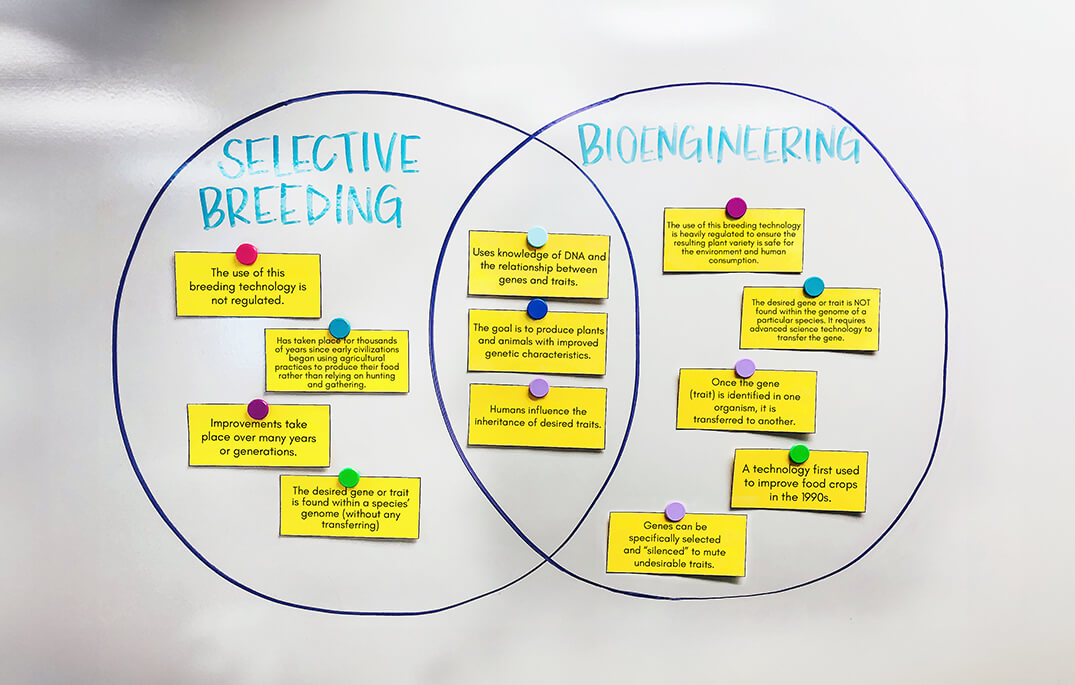
Students identify technologies that have changed the way humans affect the inheritance of desired traits in organisms; compare and contrast selective breeding methods to bioengineering techniques; and analyze data to determine the best solution for cultivating desired traits in organisms.
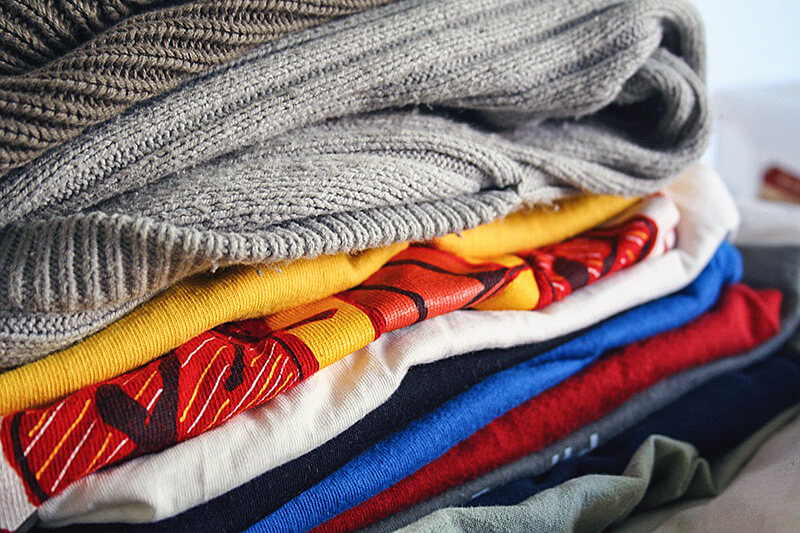

Students will gain a broad understanding of the types and sources of different fibers, examining their origins and observing their differences. Activities in this lesson include examining clothing and clothing labels and observing how different types of fabrics burn.

Students observe the anatomical structures of flowers and explain a flower's role in plant growth and reproduction as well as their connection to our food supply.

Students focus on the science involved in the production of our food and explore the high-tech aspects of agricultural production as they learn about careers in food science.

Students will explore the steps and processes that create a food system and gain an understanding of hunger as it relates to the physical well-being, culture, and geographic location of all people. Students will learn what a food system encompasses, create a "food system chain," and discuss why hunger still exists despite modern advances that have made the US food system highly efficient.
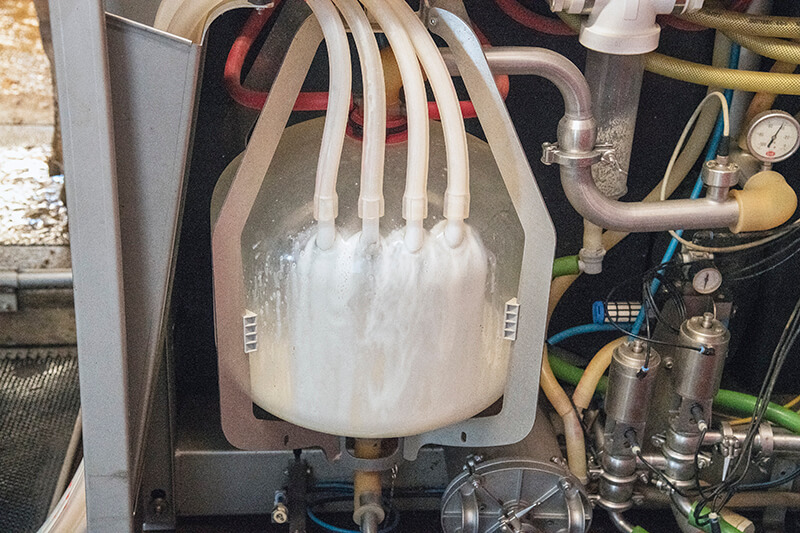
Students will explore milk production in the United States and explain the benefits of homogenization, pasteurization, and fortification of milk.

Students will participate in a foraging activity, gaining perspective on how scarcity of resources can affect well-being and how agriculture provides the benefit of a steady, reliable food supply. Then they will read about hunter-gatherers and early agriculture and use maps to explore how geography affected the development of early civilizations.
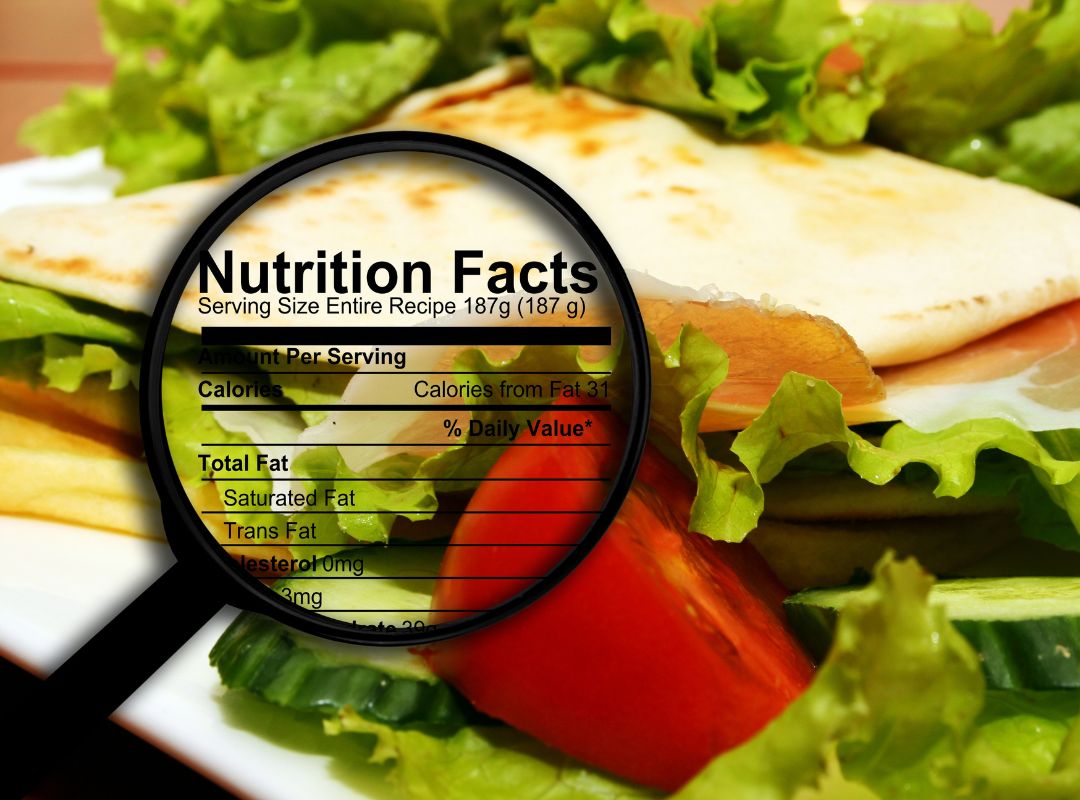
Explore the features of the Nutrition Facts label with a focus on protein, analyze serving size, and make a Nutrition Facts label for a smoothie.

In this lesson students will learn about plant parts and how they function in plant growth and reproduction.

Students will demonstrate understanding of the importance of the relationship between producers and consumers by explaining how agricultural supply and demand affects commodity prices.
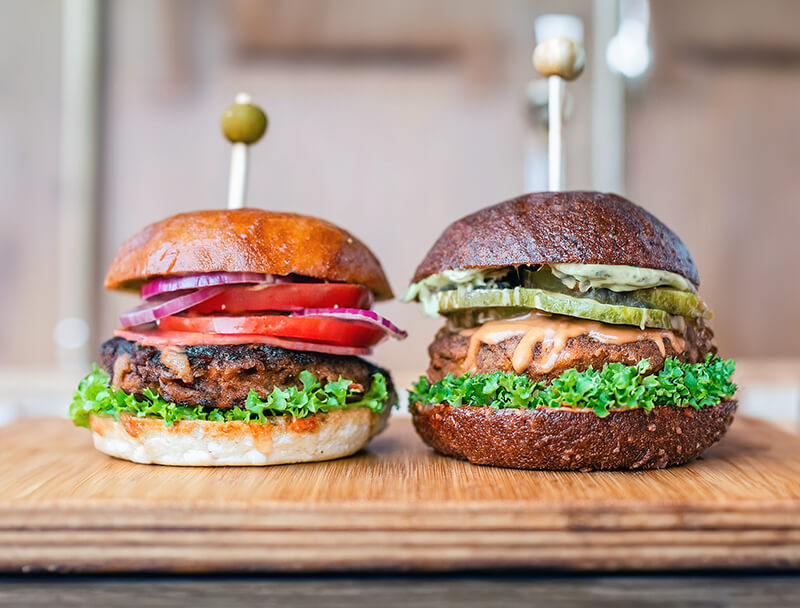

Students compare the components of beef and plant-based burgers by determining the production and processing methods of each product; evaluate the ingredients and nutritional differences between beef and plant-based products; and discuss different points of view in the agricultural industry concerning plant-based proteins and traditional beef. This lesson covers a socioscientific issue and aims to provide students with tools to evaluate science within the context of social and economic points of view.

Students will discover the five culinary functions of eggs by completing a cooking lab comparing recipes with and without eggs. Students will see how eggs leaven, bind, thicken, coat, and emulsify our foods.

While many view bioengineered crops (GMOs) as a promising innovation, there is controversy about their use. This lesson provides students with a brief overview of the technology, equipping them with the ability to evaluate the social, environmental, and economic arguments for and against bioengineered crops (GMOs). This lesson covers a socioscientific issue and aims to provide students with tools to evaluate science within the context of social and economic points of view.
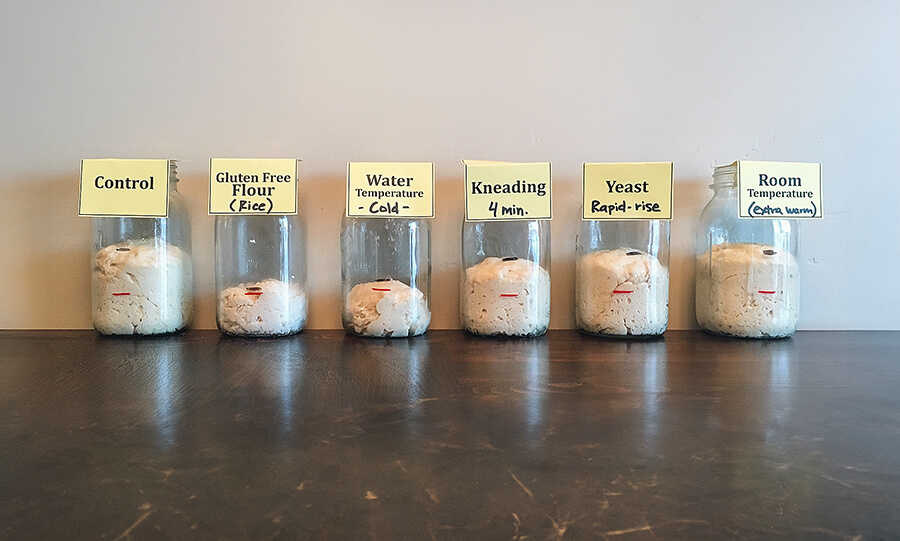

Students explore the phenomenon of what makes bread dough rise. Using baker's yeast, students will observe alcoholic fermentation and its connection to cellular respiration as they are challenged to act as food scientists and develop the best recipe for quick-rising bread dough.

In this lesson students will recognize the difference between a spice and herb, learn how herbs and spices are grown on farms around the world, and participate in a culinary challenge to season popcorn for various cultural cuisines.

Students will explore the question, “How will we sustainably feed nearly 10 billion people by the year 2050?” as they discover what sustainable agriculture is and how it is critical to securing a stable food supply and future for a growing population.

Discover how technological advances and economic forces influence the size of farms in the United States. Evaluate the pros and cons of large-scale agriculture for the production of our food, fuel and fiber and identify the similarities and differences in commercial vs subsistence farming.
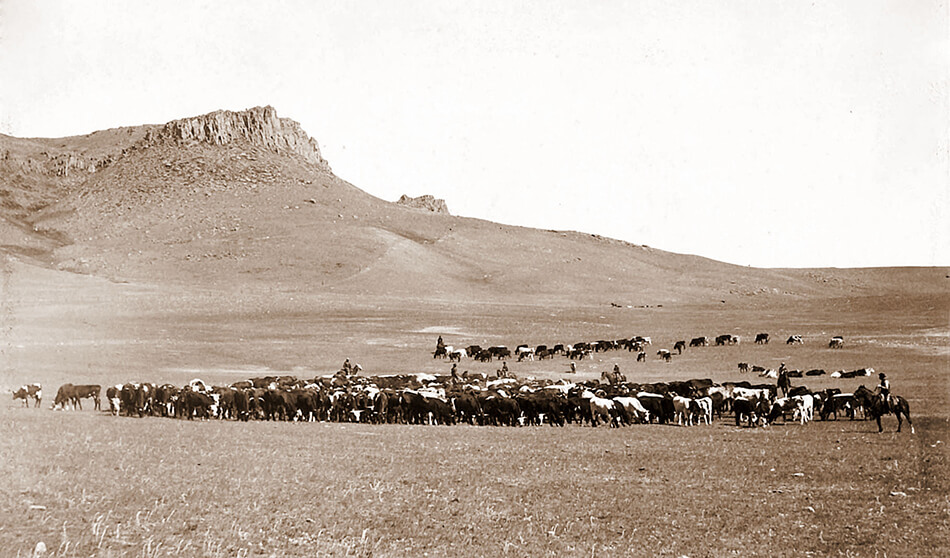

Students will gain a greater understanding of the historical context and purpose of the cattle drives that took place in the mid 1880s. Students will be able to explain the cause and effect relationships of life on the frontier including, population growth, and later the invention and use of barbed wire, refrigeration, and railroads.
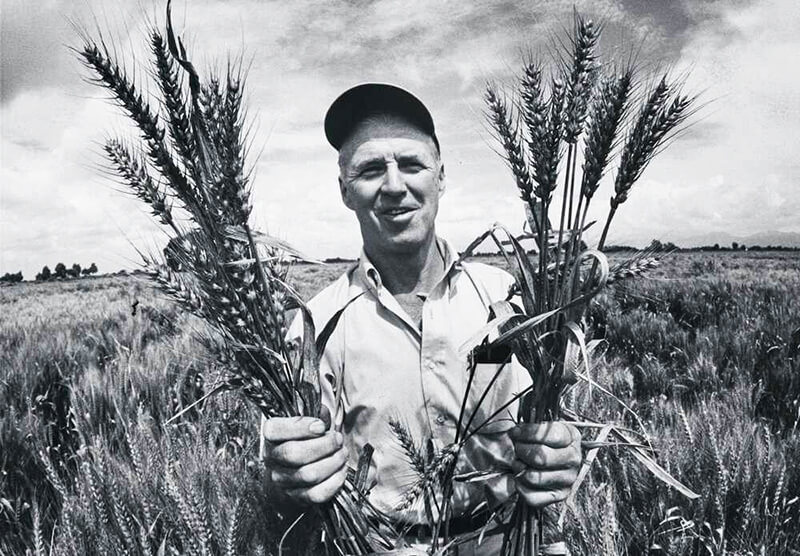

Evaluate the agricultural advances of the Green Revolution, discover the contributions of Norman Borlaug, and discuss the impacts of this era from an economic, social, political, and environmental perspective by watching the 2020 PBS film, The Man Who Tried to Feed the World.
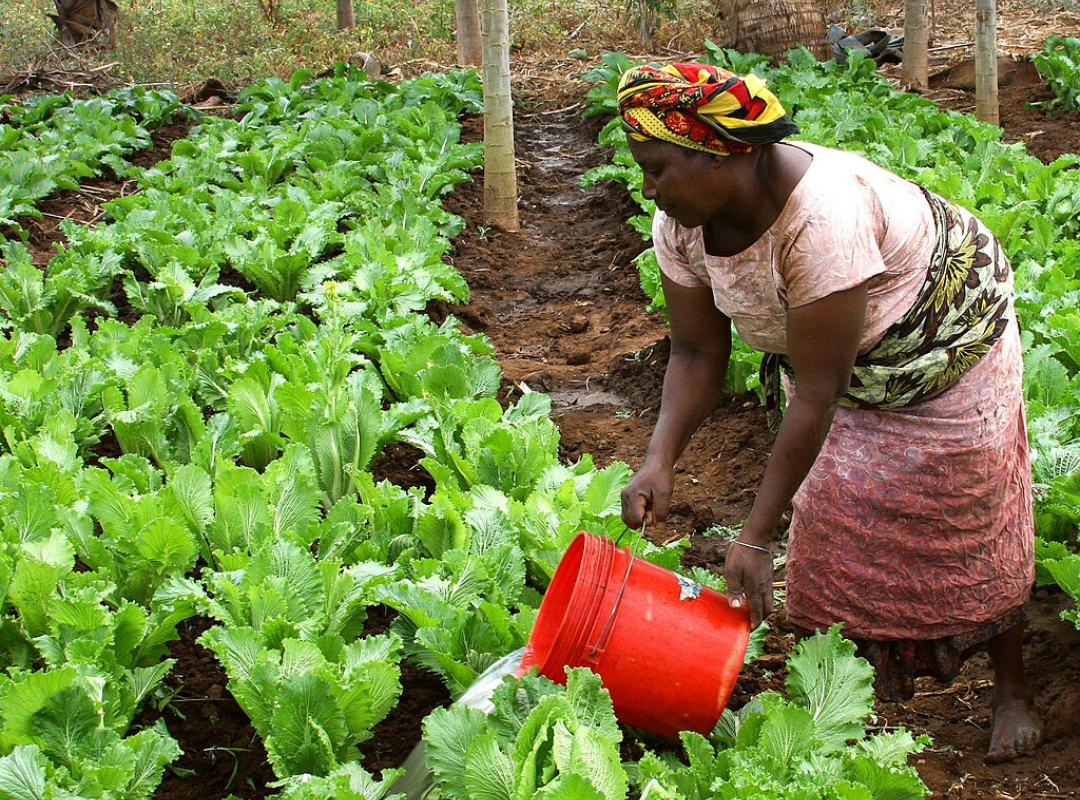

Students will investigate the number of women farmers globally and identify these farmers’ impacts on feeding the world's population.

Explore the complexity of global commodity chains that link the production and consumption of agricultural products. Discover how economics, politics, infrastructure, and other conditions affect the distribution of food throughout the world.

Students will be introduced to the Nutrition Facts label, navigate and decipher the Nutrition Facts label, use food labels to determine nutritive value of foods, and define terminology found on the label such as calories, nutrients, and servings.
A few of our all-time favorite lessons for teaching the basics of agriculture.
Students determine that agriculture provides nearly all of the products we rely on in any given day by participating in a relay where they match an everyday item with its "source."
Students use the visual representation of a web to explore the role of agriculture in their daily lives and understand how most of the necessities of life can be traced back to the farm.
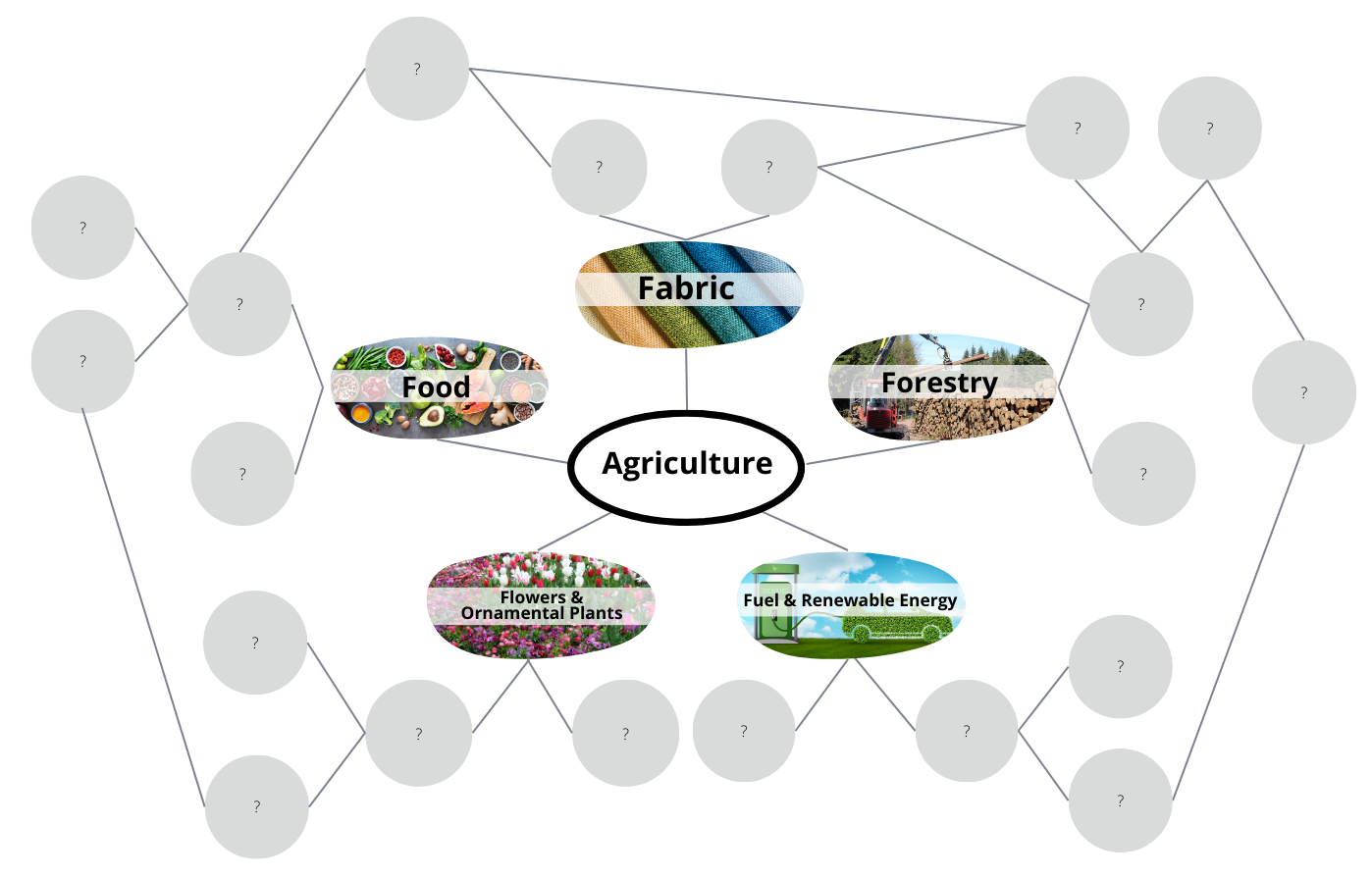
Explore how we are each connected to agriculture through our food, clothing, shelter, fuel, and more. Students will be introduced to agriculture and begin to recognize the depth and complexities of agricultural systems locally and globally.
Let us know if you have an idea you'd like to share for a new lesson plan or companion resource.
Download a CSV spreadsheet containing the vocabulary words used in the Curriculum Matrix.