Agricultural Land Use
Students explore the impact of fertilizer on algae growth, soil erosion, and agricultural soil and water conservation practices.
Students explore the impact of fertilizer on algae growth, soil erosion, and agricultural soil and water conservation practices.
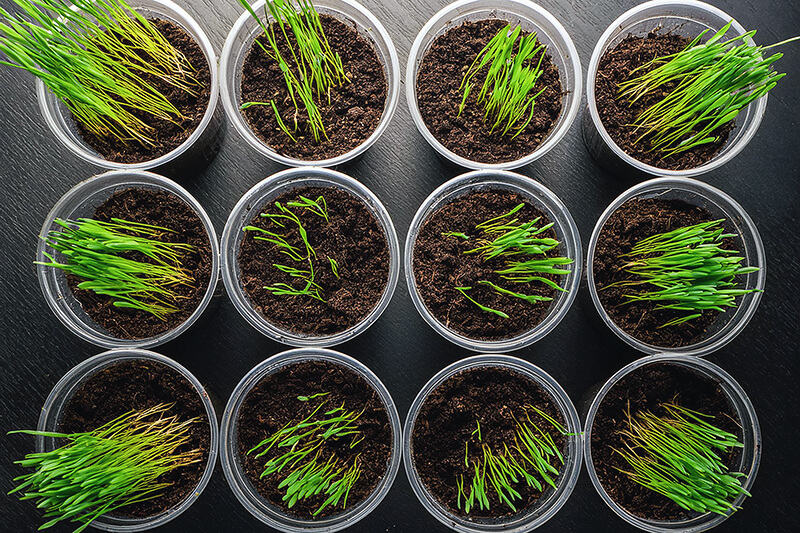

Students investigate rangelands by growing their own grass to represent a beef or sheep ranch.
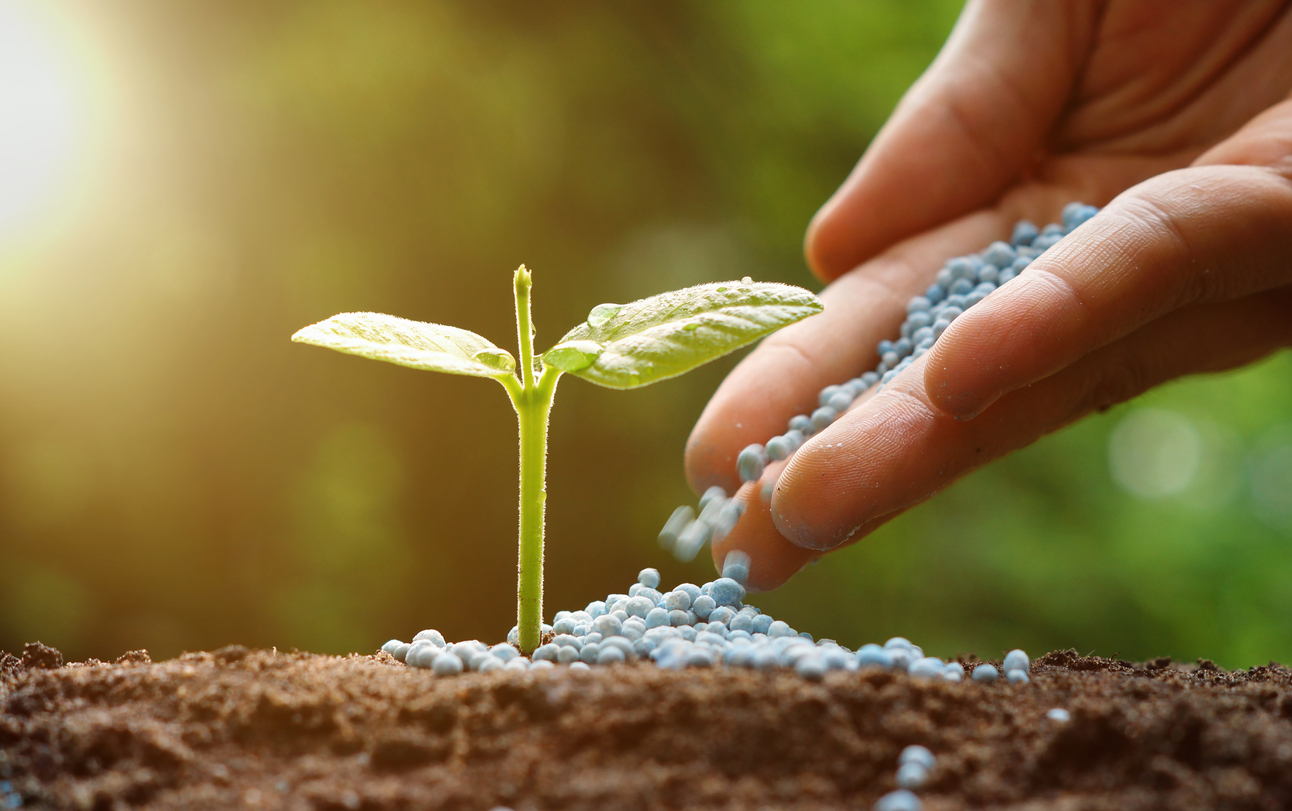

In this lesson students will recognize that fertile soil is a limited resource to produce food for a growing population, describe the role fertilizer plays to increase food productivity, distinguish between organic and commercial fertilizers, and recognize how excess nutrients are harmful to the environment.

Students will recognize that fertile soil is a limited resource, describe the role fertilizer plays in increasing food productivity, distinguish between organic and commercial fertilizers, describe how excess nutrients are harmful to the environment, and identify different sources of nutrient pollution.
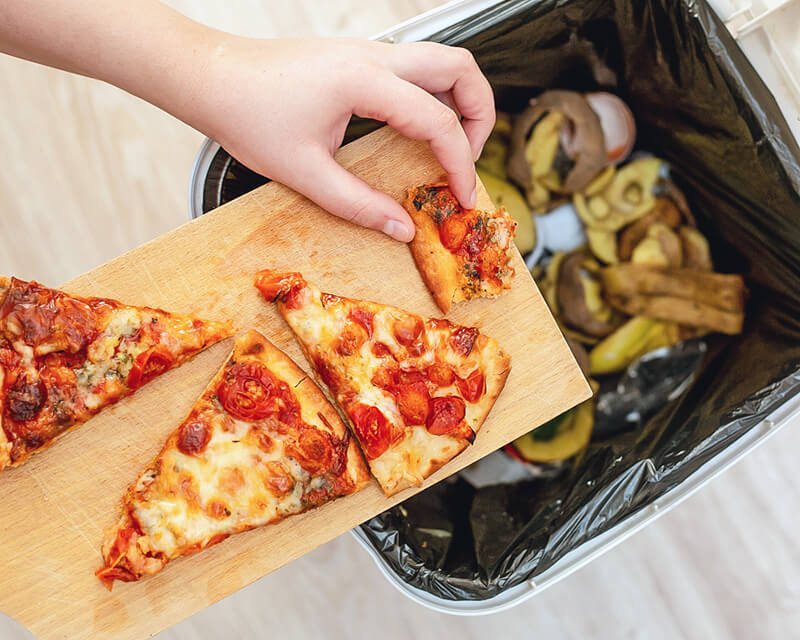

Students will explore strategies that can decrease food waste at home and school, design solutions for schoolwide food waste reduction efforts, and participate in food waste challenges that encourage sustainable shopping, correct food storage practices, and meal planning.
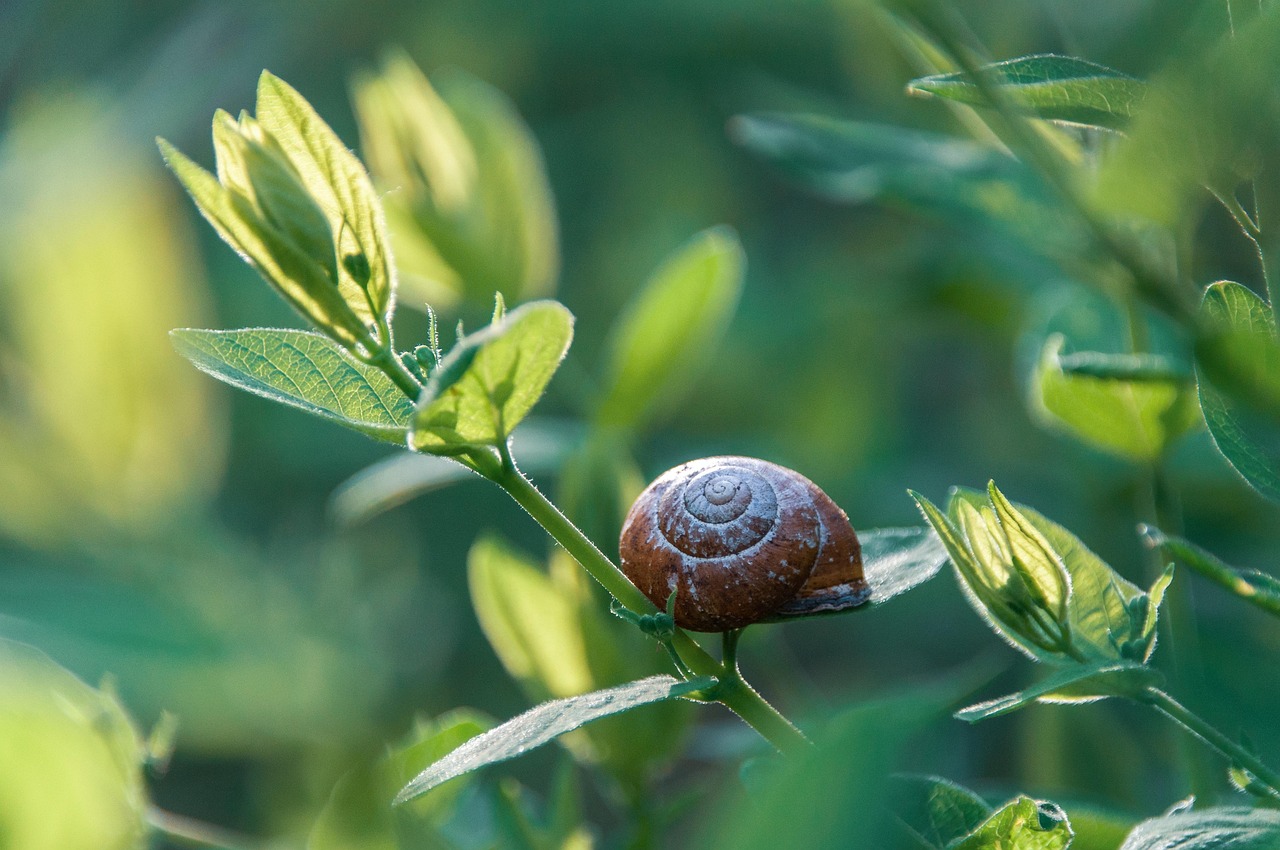

This lesson teaches about invasive species: what they are, the threats they pose, and damages they can cause. Students will identify individual pests and invasive species and discover what they threaten, where they live, and the pathways hungry pests use to enter new locations. Finally students move into action and explore what they can do to prevent the spread of invasive species.

Students will explore the core question, “How will we sustainably feed nearly 10 billion people by the year 2050?” as they discover what sustainable agriculture is and how it is critical to securing a stable food supply and future for a growing population.

Students will discuss the limited amount of fresh water on earth, identify how best management practices can reduce water consumption, discuss the need for water conservation and protection, and compare and contrast methods of irrigation for water conservation.

Students will discuss the limited amount of fresh water on earth, identify how best management practices can reduce water consumption, discuss the need for water conservation and protection, and compare and contrast methods of irrigation for water conservation.
Students will recognize that arable land (ideal land for growing crops) is a limited resource, identify best management practices that can be applied to every stakeholder’s land-use decisions; and analyze and discuss the impacts of food waste on our environment.

Students will recognize that arable land (ideal land for growing crops) is a limited resource, identify best management practices that can be applied to every stakeholder’s land-use decisions; and analyze and discuss the impacts of food waste on our environment.
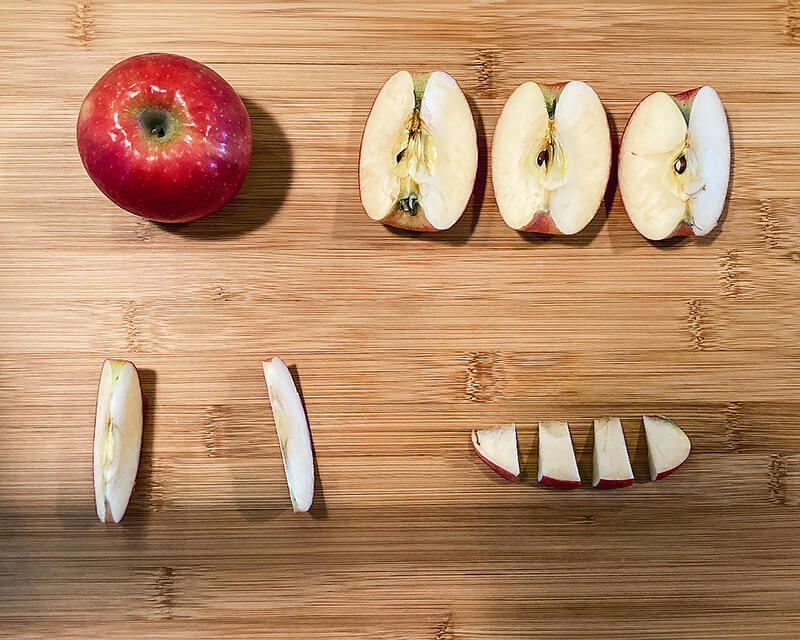

Students use an apple to represent the Earth and discover how our land resources are used. Through critical thinking, students discover why topsoil is a nonrenewable resource, the importance of soil to our food supply, and factors that impact topsoil distribution in different regions.