What? No Soil?
After learning the five basic requirements of plant growth, students discuss terms related to hydroponics. Students then build and maintain hydroponic units from soda bottles.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Minnesota Agriculture in the Classroom
Sources
Adapted from Technology, Life and Careers Agricultural Science and Technology Instructional Guide, project of the Utah State Office of Education. Protect Director Richard M Joerger, PhD., developed and written by Brenda Mager and Kari Osterhout, 1995.
Bugbee, Bruce and Gus Koerner. Teaching Hydroponic Science. “Inexpensive Hydroponic Teaching Methods” by David R. Hershey. (27-33)
Hershey, David R. “Solution Culture Hydroponics: History and Inexpensive Equipment.” The American Biology Teacher, Volume 56, No. 2, Feb 94 (111-118).
Standards
National Content Area Standards
- Career & Technical Education
- AFNR (Grades 6-8): Plant Science Systems Career Pathway
- PS.03.01: Demonstrate plant propagation techniques in plant system activities.
- AFNR (Grades 6-8): Plant Science Systems Career Pathway
- Science
- MS-ETS1: Engineering Design
- MS-ETS1-1: Define the criteria and constraints of a design problem with sufficient precision to ensure a successful solution, taking into account relevant scientific principles and potential impacts on people and the natural environment that may limit possible solutions.
- MS-LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
- MS-LS1-5: Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how environmental and genetic factors influence the growth of organisms.
- MS-LS1-6: Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for the role of photosynthesis in the cycling of matter and flow of energy into and out of organisms.
- MS-LS1-7: Develop a model to describe how food is rearranged through chemical reactions forming new molecules that support growth and/or release energy as this matter moves through an organism.
- MS-LS2: Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics
- MS-LS2-5: Evaluate competing design solutions for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- MS-ETS1: Engineering Design
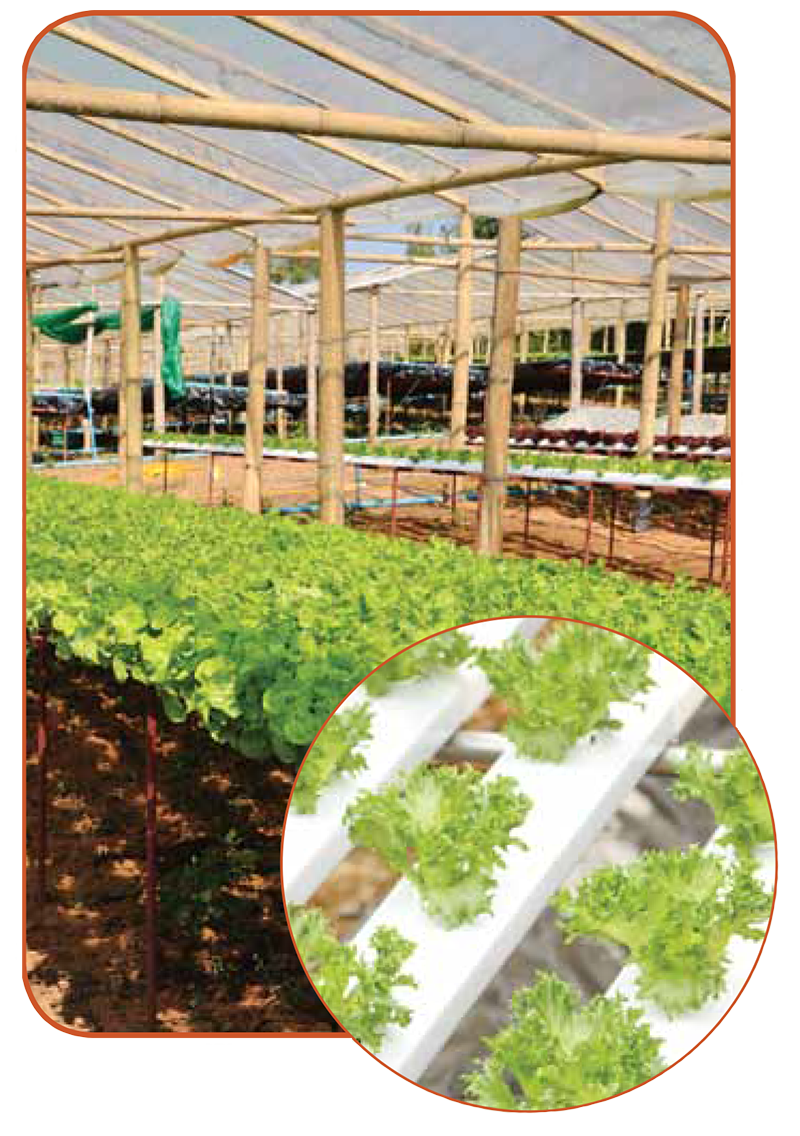 The word “Hydroponics” refers to two Greek words, “water” and “working.” It is defined as the science of growing plants without soil.
The word “Hydroponics” refers to two Greek words, “water” and “working.” It is defined as the science of growing plants without soil.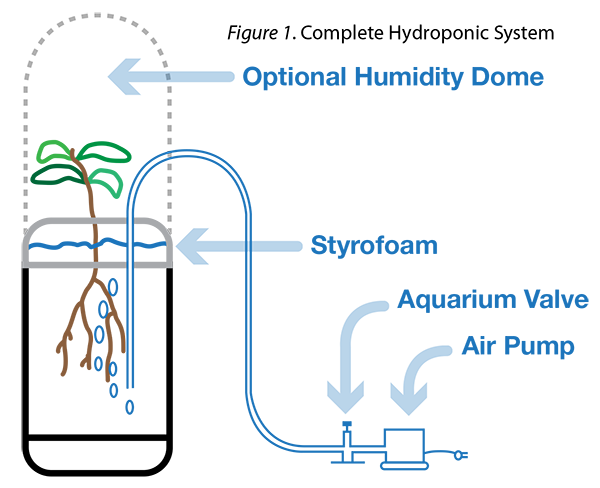 Formative Review:
Formative Review: