This lesson is part of a series called, Edible Plant Parts. These lessons allow students and teachers to examine the six basic plant parts—roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds—in a unique way. Through hands-on activities, students will learn about the different plant parts, as well as how to include fruits and vegetables into their daily meals as part of a healthy diet. Students will also learn about agriculture and the people who produce our food. The remaining lessons can be found at the following links:
Students will be fascinated to learn how nutritious and delicious eating fruits can be as a snack or with their meal. A fruit is the sweet and fleshy product of a flowering tree or plant that contains seeds and can be eaten as food. Due to technology and refrigerated transportation, fruits can be eaten in their freshest form throughout the year. For this lesson student's experience for eating fresh or canned fruits would be required for helping them gain an understanding of people who produce our food, where fruits are grown, and fruit's nutritional value.
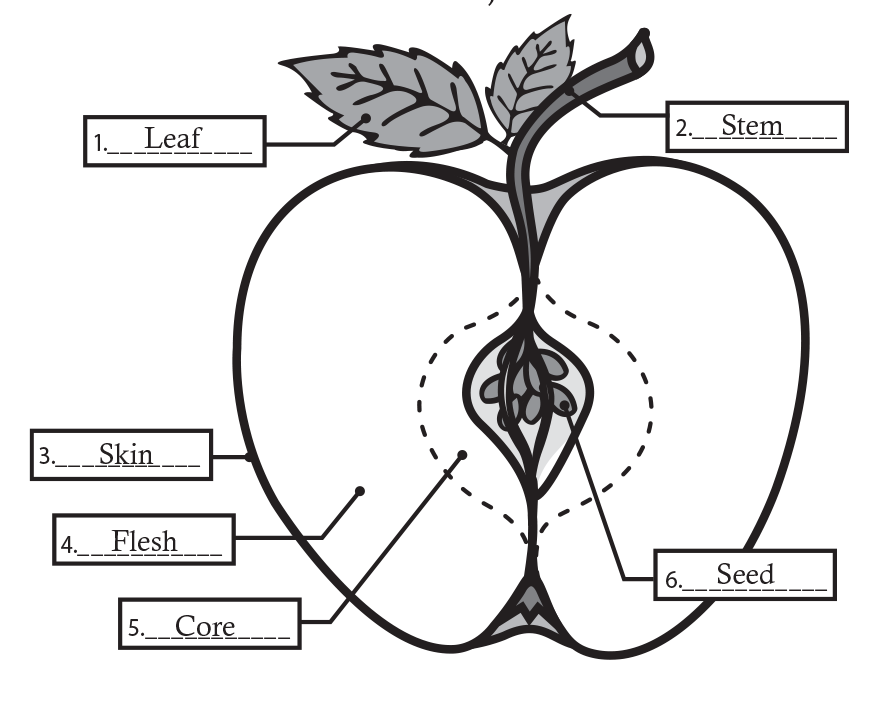
The reproductive part of a plant known as a flower, not only look pretty but they also produce fruits that we eat. When eating fruits they are low in calories, high in nutrition, high in fiber, and taste delicious. Fruits are also added in many other foods that we enjoy such as ice cream, yogurt, fruit juices, muffins, and vinegar.
Fruits are an excellent source of vitamins, known as essential nutrients used to help regulate body processes in our diets. Vitamin C helps the body heal wounds and lowers the risk of infection. It also helps keep the body from bruising and builds the tissue that holds muscles and bones together. Known as ascorbic acid, Vitamin C also helps the body absorb the iron found in foods and strengthens the immune system. Some fruits, mainly citrus such as oranges, grapefruits, and lemons also contain citric acid which acts as a natural preservative.
Crops that are usually listed as fruits are grown on trees, shrubs, or vines and produce fruit for a number of years. These include apples, apricots, avocados, cherries, dates, berries, figs, grapes, lemons, nectarines, olives, oranges, and pears. The fruit of a plant generally surrounds the seeds of a plant. The fruit protects the seeds and attracts animals and insects. When animals eat the fruit they usually also eat the seed, which will later be deposited with the animal’s scat, or waste. The scat provides nutrients for the seed to grow into a plant. This process helps disperse seeds and plants to new areas. For example, birds might eat berries in one location, then fly to another location and deposit their scat with the berry seeds in the new location. A person might pick an apple from a tree, then carry it to a different place to eat, and drop the seeds in this new location.
Today, Californians and others across the United States are fortunate to have access to fresh fruit year round because the climate, or weather conditions are ideal. This wasn’t always the case. When the gold rush in California began in 1849, hundreds of thousands of people began to move west to California seeking their fortunes in the gold mines. These miners and their families lacked fresh foods, especially those rich in vitamin C. A lack of vitamin C causes a disease called scurvy. Symptoms of scurvy include general weakness, bleeding of gums, and rupture of capillaries under the skin. In the gold rush days, citrus juice was often prescribed as a medical cure for scurvy and was sold for $1 an ounce.
While many miners did not strike it rich in gold, some discovered that the fertile soil in many parts of California was ideal for farming. Many crops were planted, including fruit orchards in order to meet the demand for fresh fruit from miners and settlers. Modern refrigeration was not yet available to keep fruit fresh after it was picked. Canning was the method used to preserve fruit after harvest so it could be eaten throughout the year and shipped to consumers in other parts of the state. Today, shipping of produce has become much faster and efficient than in the 1800s, and both fresh and canned fruit are readily available in our grocery stores all year long. California is the leading agricultural state in the nation, growing over 400 crops.