Fruits contain important disease-fighting compounds called antioxidants. Antioxidants aid in the prevention and repair of cells damaged from oxidation. Oxidation is a normal process that our body’s cells undergo, but it can cause stress on our bodies. It is important to eat foods containing antioxidants to help keep our bodies healthy and to treat and prevent the stress caused by oxidation. Antioxidants can be found in fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and spices. Fruits containing the highest concentrations are berries, such as cranberries, blueberries, and blackberries. Including these foods in our diets may help prevent diseases, including cancer and heart disease.

Vitamins and Antioxidants
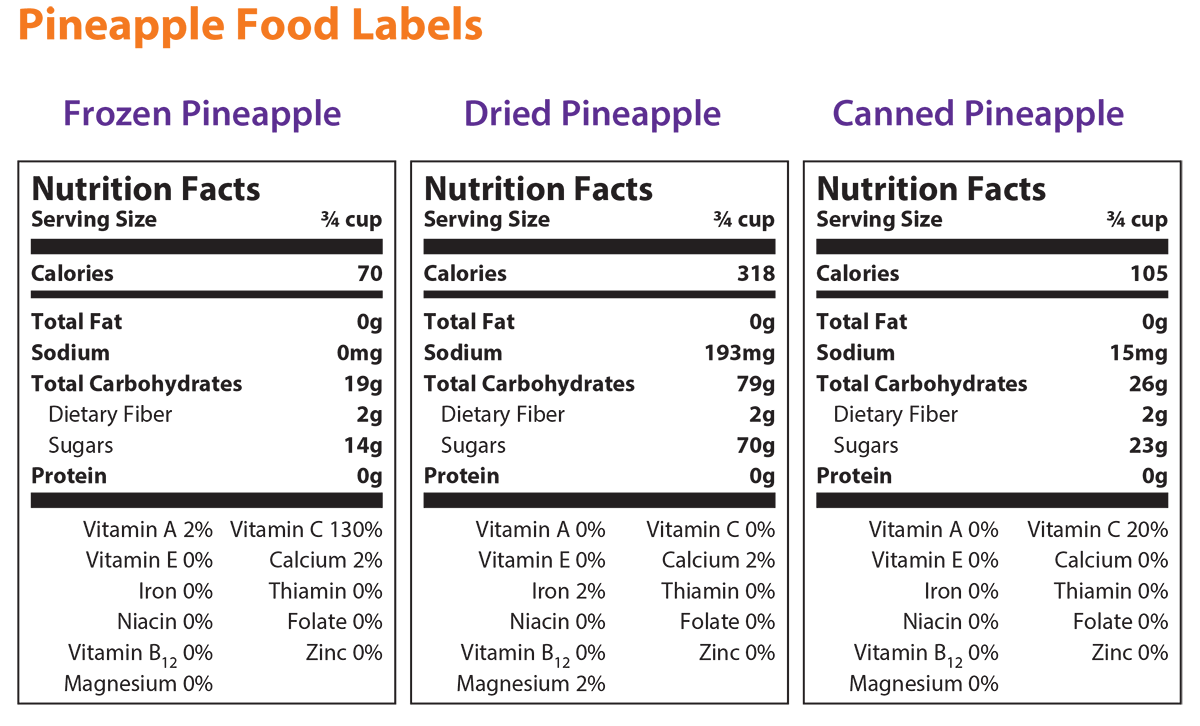
Vitamins A, C, E, and the mineral zinc are antioxidants that can be found on the nutrition facts label. Vitamin C is the most common antioxidant, and it helps heal cuts and protect bones and teeth. Citrus fruits, including grapefruit, lemons, limes, oranges, and tangerines, are the highest in Vitamin C. Vitamin A is found in colorful fruits, like apricots and cantaloupe. Vitamin A helps your eyes. Vitamin E and zinc help your immune system and can be found in many different foods. The mineral selenium and the phytochemicals (see FoodMASTER Middle: Vegetables) lycopene, beta-carotene, and flavonoids are also antioxidants found in fruit.
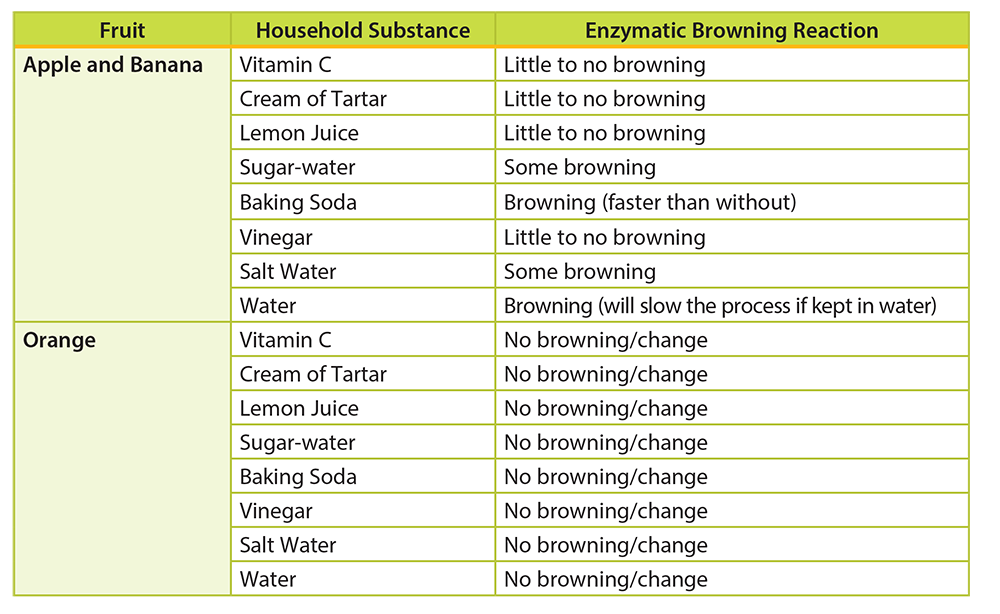
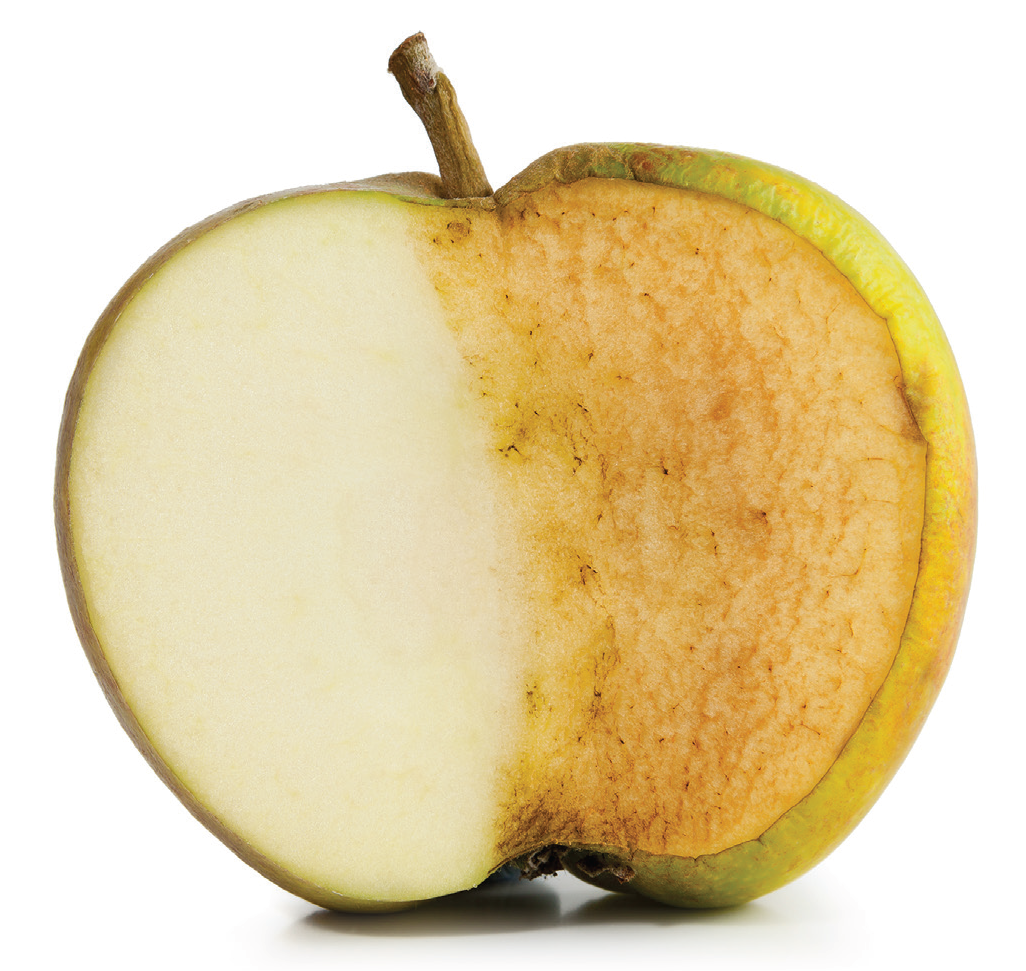
Some of the antioxidants found in fruits (and some vegetables) have also been found to prevent other damaging processes, like enzymatic browning. Enzymatic browning occurs when enzymes catalyze the oxidation of phenols causing a food’s color to change to brown. Enzymatic browning can be both beneficial and detrimental for foods; however, it is not considered unhealthy to consume these foods after they have turned brown. For foods like tea and dried fruits, enzymatic browning is beneficial; it enhances their flavor and color. For foods like fresh fruits, vegetables and seafood, enzymatic browning is unfavorable because the brown color change causes them to appear aged.
Methods to Prevent Enzymatic Browning Reactions Application of Heat
- Application of Heat: Blanching - Fruits and vegetables are often boiled for 1-5 minutes (depending on size of produce) before freezing. Blanching inactivates enzymes by causing these proteins to denature and lose function.
- Sulfur Dioxide Dip: Sulfur dioxide is able to stabilize the color of fresh, and also processed fruits and vegetables. Sulfur dioxide stops the activity of oxidizing enzymes by removing the oxygen from the enzyme before pigments are formed. Sulfur dioxide also has antioxidant properties. It is often used in salad bars at restaurants to prevent unattractive browning.
- Sugar Syrup Dip: This method is one of the oldest to prevent browning. The sugar syrup coats the fruit and prevents the fruit surface from contacting oxygen.
- Vitamin C Dip: Vitamin C is a great antioxidant. It is oxidized instead of the catechol/tannin pigments that turn fruits brown when exposed to oxygen.
- Citric acid and acetic acid: Acids work to lower the pH of fruit tissue and reduce the action of polyphenol oxidase (browning enzyme). If the pH falls below 3.0 the enzyme will be inactivated.
FoodMASTER Middle Lessons
FoodMASTER (Food, Math and Science Teaching Enhancement Resource) is a compilation of programs aimed at using food as a tool to teach mathematics and science. For more information see the Background & Introduction to FoodMASTER for Middle School. This lesson is one in a series of lessons designed for middle school: