Plasmid Problem Solving
This lesson compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and examines the form and function of the plasmid found in prokaryotic cells. Students will then use these principles to simulate how a desirable gene can be isolated and inserted into a plasmid as one step in the process of creating a bioengineered (GMO) plant variety.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Andrea Gardner, Heather McPherson, and Mariel Sellers | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL) and Syngenta
Acknowledgements
Activity 3 was written by Heather McPherson and Mariel Sellers as part of the Syngenta Summer Fellowship Educator's Guide. The remaining activities were developed and added with permission by the National Center for Agricultural Literacy.
Sources
- https://bitesizebio.com/13522/who-found-the-first-plasmid/
- http://www.encyclopedia.com/science-and-technology/biology-and-genetics/genetics-and-genetic-engineering/plasmid
- https://gmoanswers.com/current-gmo-crops
- Pharmacogenomics. (n.d.). Retrieved October 11, 2016, from https://www.boundless.com/biology/definition/pharmacogenomics/.
- Biotechnology in Medicine - Boundless Open Textbook. (n.d.). Retrieved October 11, 2016, from https://www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/biotechnology-andgenomics-17/biotechnology-119/biotechnology-inmedicine-480-11702/.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5250645/
- “By Planting Insect resistant Cotton, Researchers Hope.” (n.d.). Insect-resistant Crops Through Genetic Engineering. Retrieved October 11, 2016, from http://www.aces.uiuc.edu/vista/html_pubs/biotech/insect.htm.
- Green, J. M., & Owen, M. D. K. (2011). “Herbicide-Resistant Crops: Utilities and Limitations for Herbicide-Resistant Weed Management.” Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59 (11), 5819–5829. http://doi.org/10.1021/jf101286h.
- “What Is Bioremediation?” (n.d.). Retrieved October 11, 2016, from http://www.hawaii.edu/abrp/biordef.html.
Standards
National Content Area Standards
- Social Studies – History
- NCSS 8 (Grades 9-12): Science, Technology, and Society
- Objective 2: Science and technology have had both positive and negative impacts upon individuals, societies, and the environment in the past and present.
- Objective 4: Consequences of science and technology for individuals and societies.
- Objective 5: Decisions regarding the uses and consequences of science and technology are often complex because of the need to choose between or reconcile different viewpoints.
- Objective 11: That achievements in science and technology are increasing at a rapid pace and can have both planned and unanticipated consequences.
- NCSS 9 (Grades 9-12): Global Connections
- Objective 6: Technological advances can both improve and detract from the quality of life.
- NCSS 8 (Grades 9-12): Science, Technology, and Society
- Science
- HS-LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
- HS-LS1-2: Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms.
- HS-LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
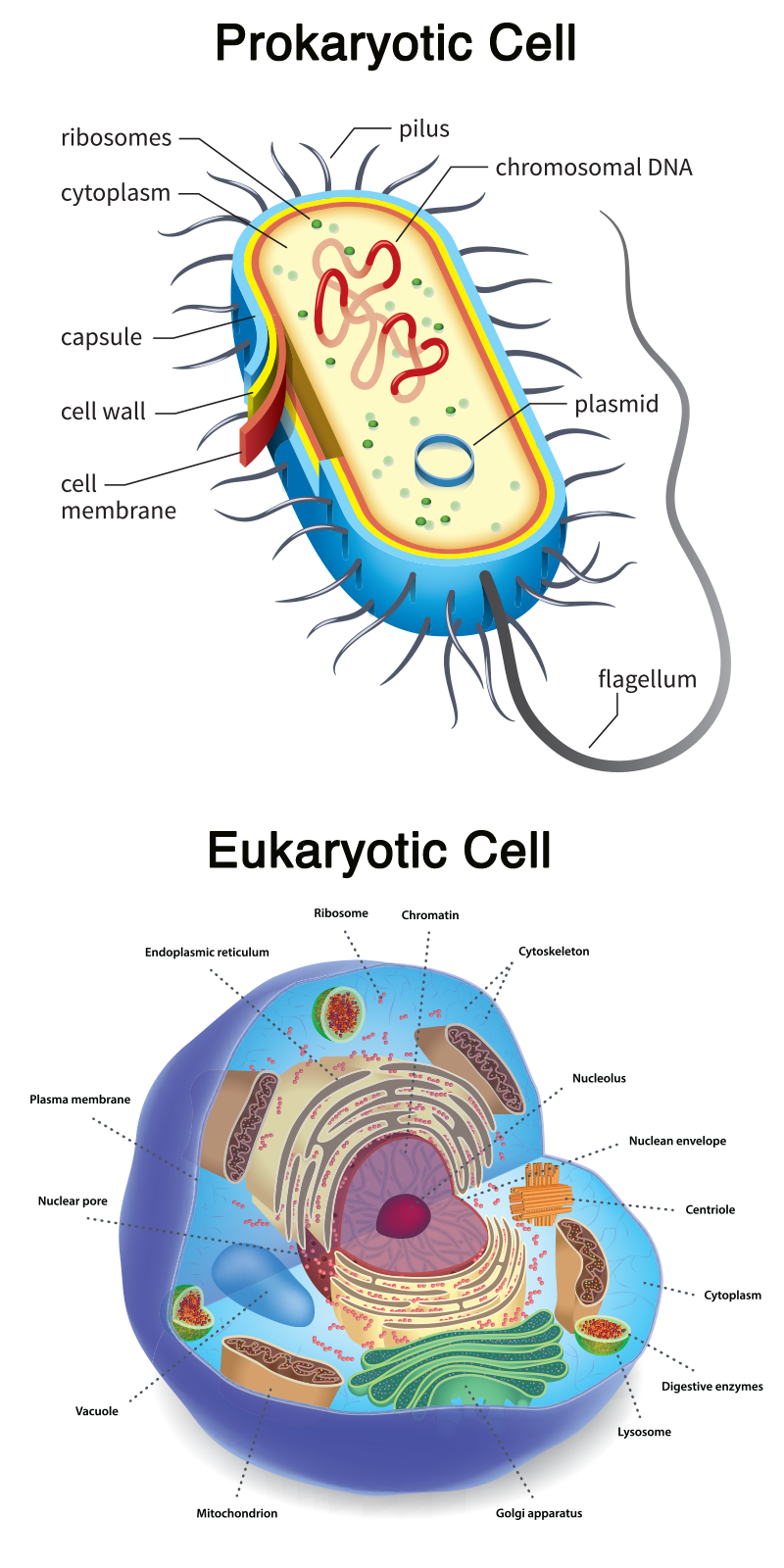 Most eukaryotic cells contain one or more chromosomes found in the nucleus of animal and plant cells. Chromosomes are made of strands of DNA, which contains the genetic code of an organism. A plasmid is a genetic structure in a cell that can replicate independently of the chromosomes. Plasmids are a small circular strand of DNA found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells such as bacterium or protozoan. While both structures contain DNA, plasmid and chromosomal DNA differ. First, plasmids have relatively few genes (less than 30) compared to chromosomal DNA. Second, plasmid DNA is not usually essential to the survival of the cell (bacteria), but instead carries genes that confer a selective advantage on their host such as a resistance to bacteria, fungi, or antibiotics. In contrast, chromosomal DNA carries essential information for the life of the cell. Third, while chromosomal DNA replicates as part of mitosis or meiosis, plasmids complete their own replication process completely separate from the chromosomes. In nature, plasmids can be passed between two bacterial strains by a set of transfer genes located on the plasmid. The proteins produced by the transfer genes bind to the DNA within the plasmid. When a break or “nick” occurs in the plasmid, the DNA unwinds and the new DNA can enter the strand bridging the gap in the plasmid DNA and potentially allowing the plasmid to inherit the new trait.2
Most eukaryotic cells contain one or more chromosomes found in the nucleus of animal and plant cells. Chromosomes are made of strands of DNA, which contains the genetic code of an organism. A plasmid is a genetic structure in a cell that can replicate independently of the chromosomes. Plasmids are a small circular strand of DNA found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells such as bacterium or protozoan. While both structures contain DNA, plasmid and chromosomal DNA differ. First, plasmids have relatively few genes (less than 30) compared to chromosomal DNA. Second, plasmid DNA is not usually essential to the survival of the cell (bacteria), but instead carries genes that confer a selective advantage on their host such as a resistance to bacteria, fungi, or antibiotics. In contrast, chromosomal DNA carries essential information for the life of the cell. Third, while chromosomal DNA replicates as part of mitosis or meiosis, plasmids complete their own replication process completely separate from the chromosomes. In nature, plasmids can be passed between two bacterial strains by a set of transfer genes located on the plasmid. The proteins produced by the transfer genes bind to the DNA within the plasmid. When a break or “nick” occurs in the plasmid, the DNA unwinds and the new DNA can enter the strand bridging the gap in the plasmid DNA and potentially allowing the plasmid to inherit the new trait.2 Image source
Image source 

