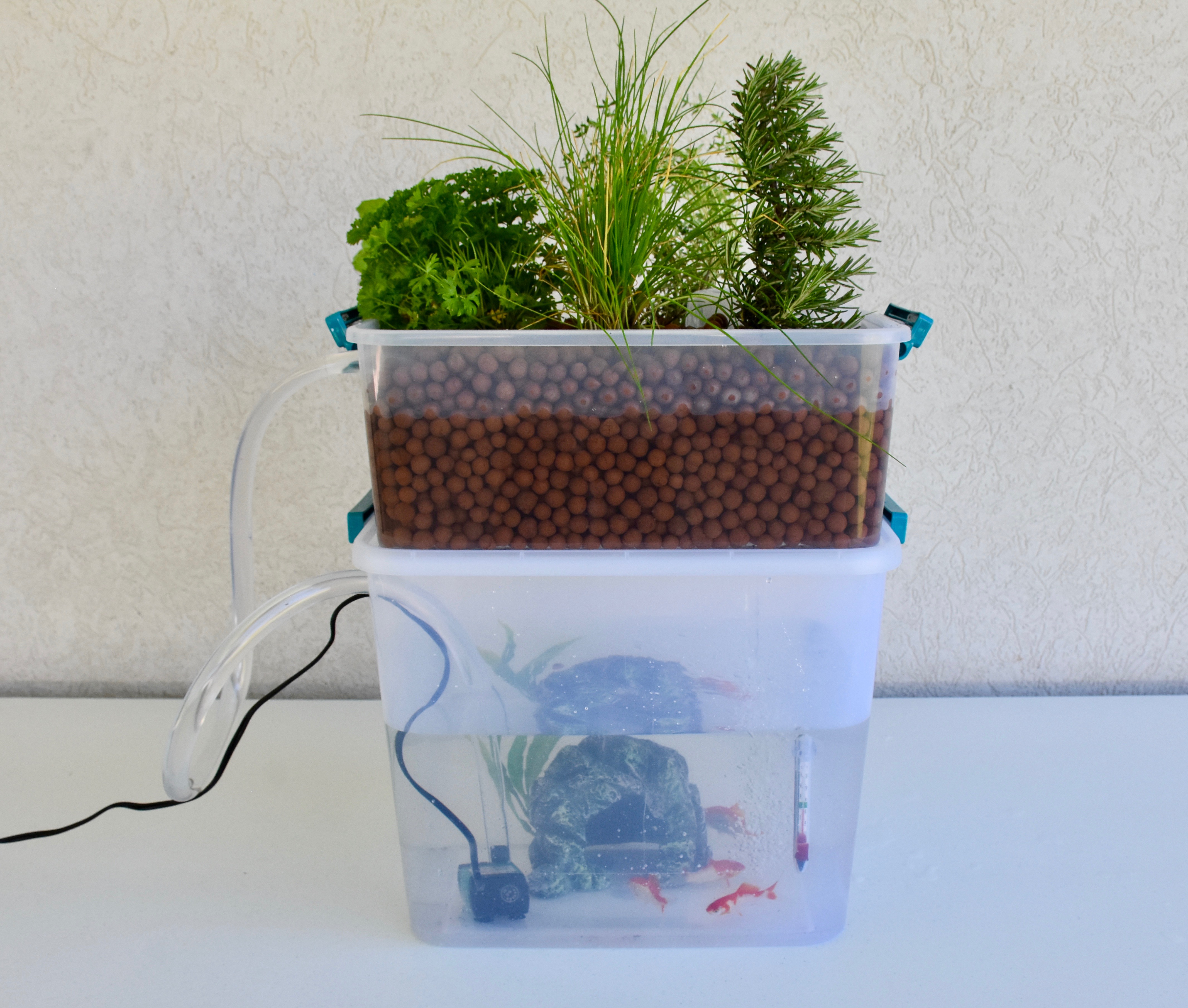
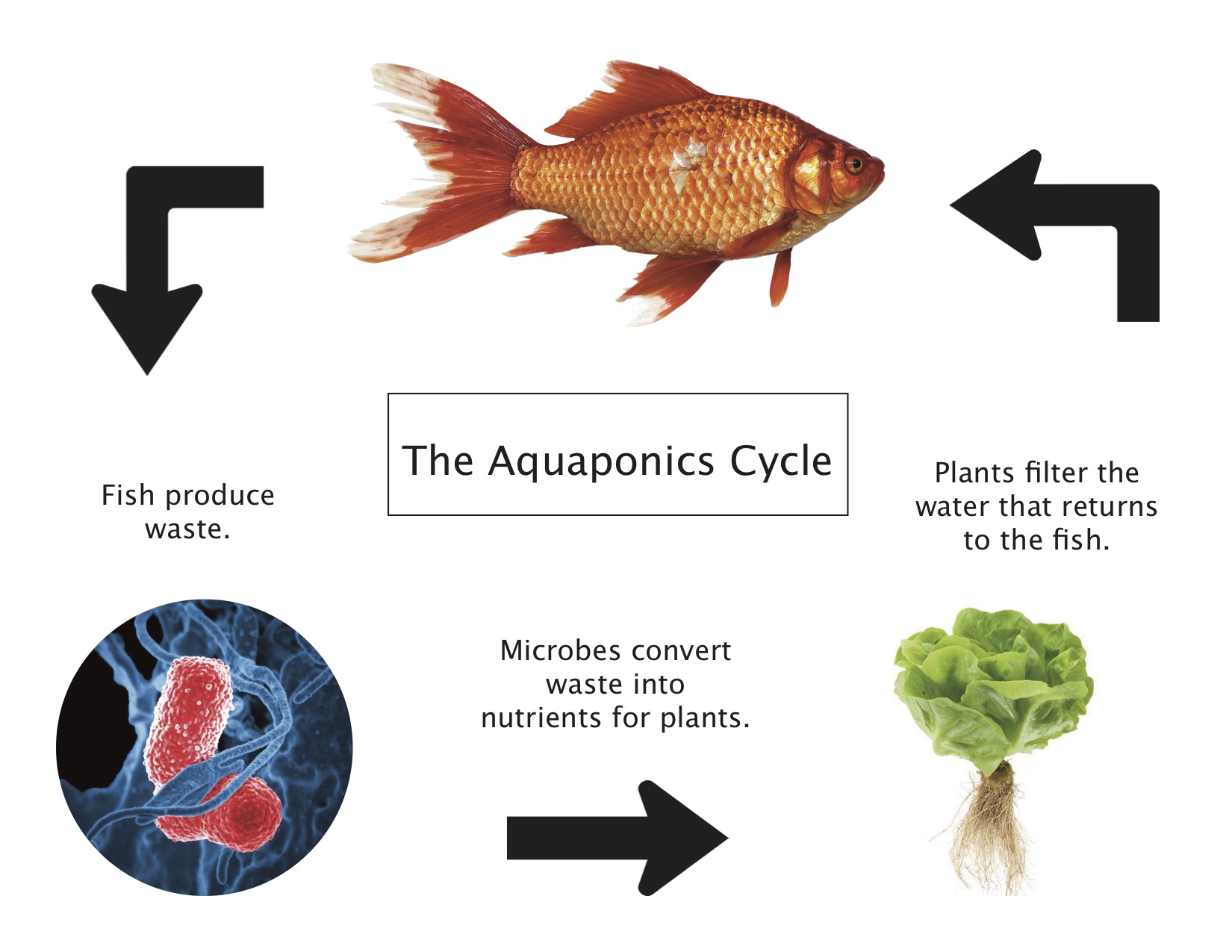
Aquaponics is the combination of aquaculture (farming fish and other aquatic organisms) and hydroponics (growing plants in water without soil). Fish and plants are simultaneously grown in an enclosed, recirculating system. A small-scale aquaponics system has ten basic components—a fish tank, a grow bed, a growing medium, a water pump, tubing, a grow light, a fish cave, water, fish, and plants. Water from the fish tank is pumped to the plants, removing the waste from the fish and keeping the fish tank clean. The fish waste is converted by bacteria into a natural fertilizer that is absorbed by the plants. The water is filtered through the plant roots and returned back to the fish tank, providing the fish with a fresh source of water. The fish and plants interact in a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship within a single system. The waste produced by one is used by the other. With the exception of the fish food, all fish and plant needs are provided within the aquaponics system.
Plants require nutrients, water, air, and light to survive and grow. Nutrients, sometimes referred to as fertilizers, are the vitamins and minerals plants need for healthy growth. They come from the decomposition of rocks, dead plants, and animals and are absorbed through the roots of the plant. Water is also absorbed through the roots and transported to the rest of the plant through the stem. Water helps keep plants rigid and transports nutrients throughout the plant. Air enters the plant through tiny holes in the leaves called stomata. The roots absorb oxygen to convert food into energy, a process called respiration. Plants use energy from light to make food. In the photosynthesis process, the plants use energy from light, carbon dioxide from the air, and water to make sugars and starches that are used as food for the plant. In nature, plants typically get nutrients from soil, water from rain, carbon dioxide and oxygen from the air surrounding them and from air pockets in the soil, and light from the sun. In an aquaponics system, nutrients come from the fish waste, water comes from the fish tank, air is present in the classroom, and light comes from the grow light.
Like humans, fish have four basic needs—nutrients, water, air, and shelter. Different types of fish eat different types of food. Fish feed on microorganisms, smaller fish, worms, plankton, sponges, algae, aquatic plants, or commercial fish food. Freshwater fish do not actively drink water. The water they need flows into them through their gills and skin. Saltwater fish actively drink water through their mouths. Their bodies process the water to filter out the salt. Fish need oxygen from the air present in water to breathe. A fish breathes by taking water into its mouth and forcing it through its gill passages. As water passes over the thin walls of the gills, dissolved oxygen moves into the blood and travels to the cells of the fish. Fish need shelter for protection from predators. Some fish also eat, sleep, and spawn under the cover of shelters. In an aquaponics system, clean water comes from the water that is filtered by the plants and drained into the fish tank, air is present in the water, and shelter is provided by the rock cave in the fish tank. Nutrients are the only fish need that is not provided within the aquaponics system. Nutrients for the fish are added to the system, most often in the form of commercial fish food appropriate to the species of fish being raised.