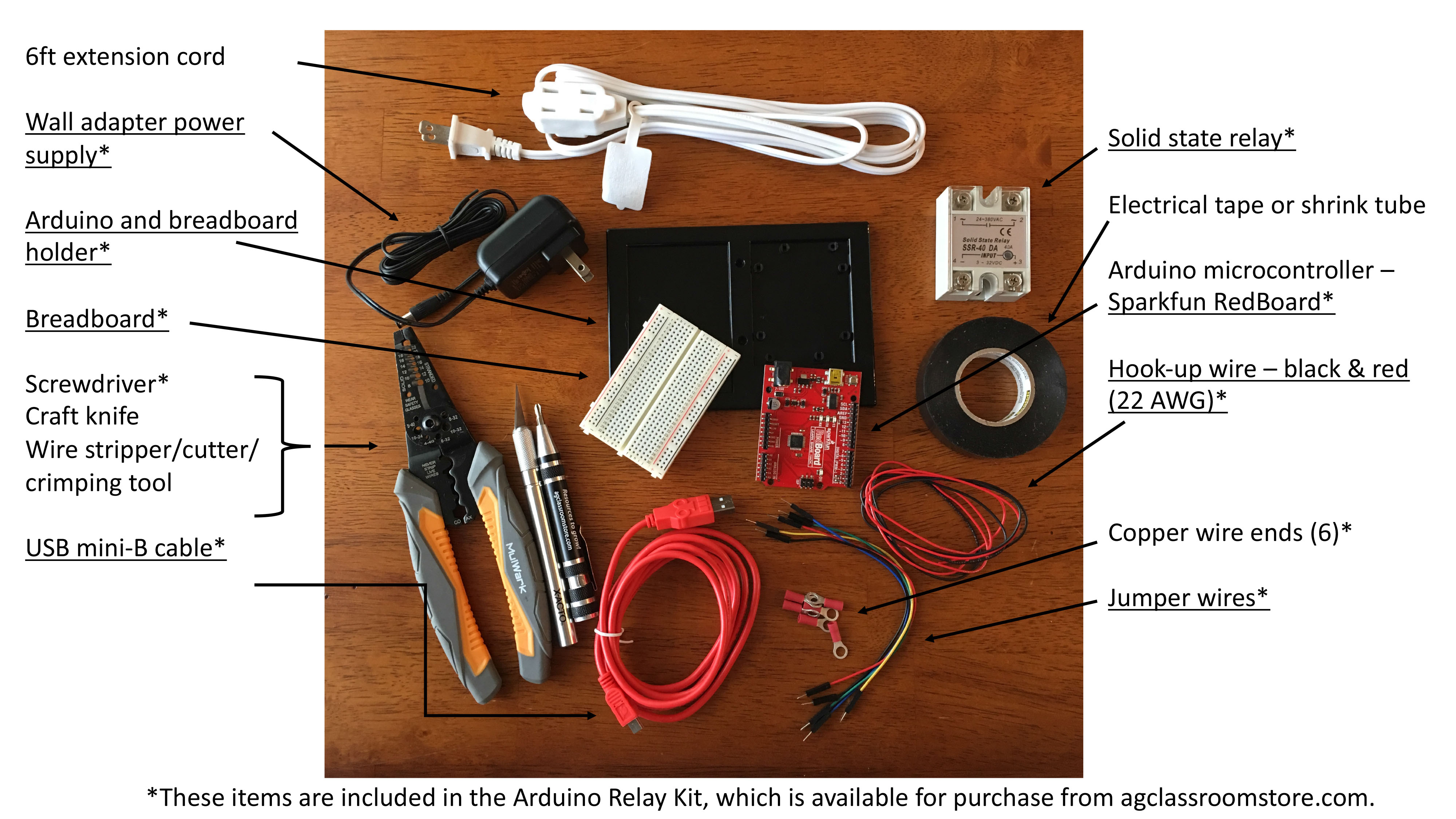
Aeroponic Engineering and Vertical Farming (Grades 9-12)
Students will use the Engineering Design Process to develop and construct an aeroponic garden to grow a food crop. Students will develop and apply an understanding of plant anatomy and physiology related to plant growth and ultimately discuss the possibilities and limitations of using vertical farming to produce our food.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Joe Furse, Andrea Gardner, and Debra Spielmaker | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Sources
Ag Facts:
- http://www.worldometers.info/water/
- Bugbee, B. (2013, November 19). Turning water into food. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qEbdv3bFKww
Background:
- http://aeroponicsdiy.com/aeroponics-misting-frequency-for-root-growth/
- http://www.aeroponics.com/siteindex2010-12.htm
- https://gardenpool.org/online-classes/how-to-make-a-simple-aeroponics-system
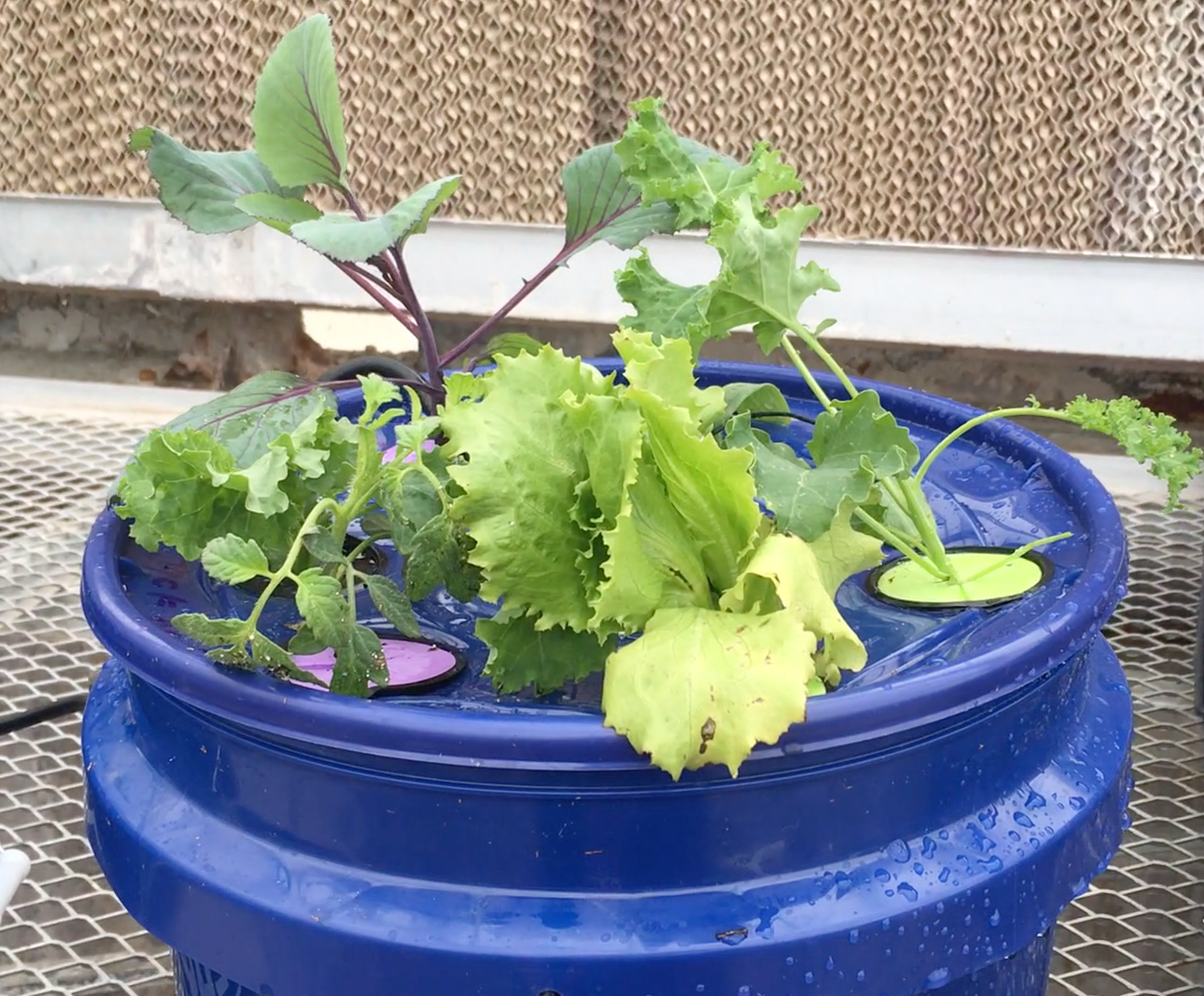
- The following link provides an example of a "5-gallon bucket Aeroponics system" that is the basis of the design challenge for this unit. https://gardenpool.org/online-classes/how-to-make-a-simple-5-gallon-bucket-aeroponics-system
- Garden Pool (n.d.) How to make a simple 5 gallon bucket aeroponics system. Retrieved from https://gardenpool.org/online-classes/how-to-make-a-simple-5-gallon-bucket-aeroponics-system
- Khokhar, T. (2017, March 22). Chart: Globally, 70% of fresh water is used for agriculture [Weblog comment]. Retrieved from https://blogs.worldbank.org/opendata/chart-globally-70-freshwater-used-agriculture
- Massie, L. (n.d.) Aeroponics misting frequency for root growth [Weblog comment]. Retrieved from http://aeroponicsdiy.com/aeroponics-misting-frequency-for-root-growth/
Standards
National Content Area Standards
- Career & Technical Education
- AFNR (Grades 9-12): Plant Science Systems Career Pathway
- PS.01.01: Determine the influence of environmental factors on plant growth.
- PS.01.03: Develop and implement a fertilization plan for specific plants or crops.
- PS.02.02: Apply knowledge of plant anatomy and the functions of plant structures to activities associated with plant systems.
- PS.03.01: Demonstrate plant propagation techniques in plant system activities.
- PS.03.02: Develop and implement a management plan for plant production.
- AFNR (Grades 9-12): Plant Science Systems Career Pathway
- Science
- HS-ETS1: Engineering Design
- HS-ETS1-1: Analyze a major global challenge to specify qualitative and quantitative criteria and constraints for solutions that account for societal needs and wants.
- HS-ETS1-2: Design a solution to a complex real-world problem by breaking it down into smaller, more manageable problems that can be solved through engineering.
- HS-ETS1-3: Evaluate a solution to a complex real-world problem based on prioritized criteria and tradeoffs that account for a range of constraints, including cost, safety, reliability, and aesthetics, as well as possible social, cultural, and environmental impacts.
- HS-ETS1: Engineering Design