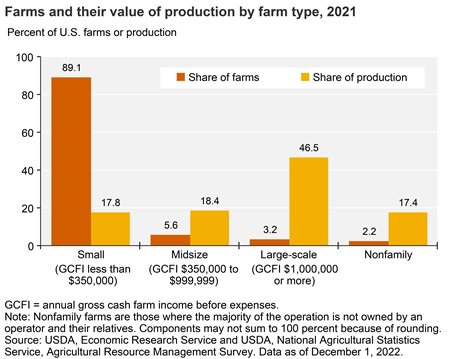
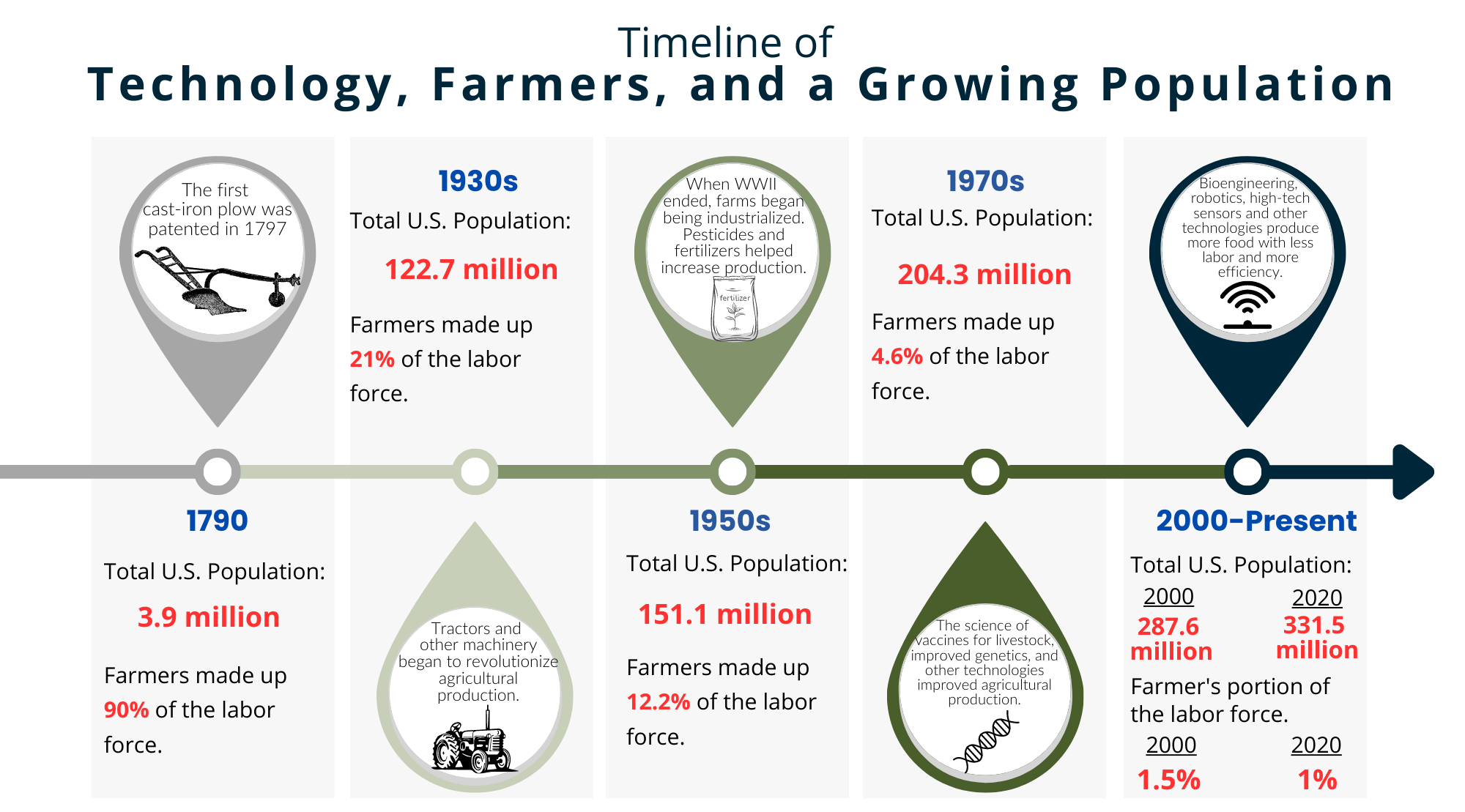
The Big Deal About Big Ag
Discover how technological advances and economic forces influence the size of farms in the United States. Evaluate the pros and cons of large-scale agriculture for the production of our food, fuel and fiber and identify the similarities and differences in commercial vs subsistence farming.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Andrea Gardner | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Sources
- Farm Size and Productivity | Our World in Data
- Small family farmers produce a third of the world’s food | FAO
- Smallholder farming is a proven path out of poverty, but climate change is changing the rules | Gates Foundation
- A Look at America's Family Farms | USDA
- Farm Structure and Contracting | USDA ERS
- Family Farms | USDA NIFA
- Farming and Farm Income | USDA ERS
- Most farms are small, but large farms account for the largest share of production value | USDA ERS
- Economies of Size in Production Agriculture | NIH
Standards
National Content Area Standards
- Career & Technical Education
- AFNR (Grades 9-12): Agribusiness Systems Career Pathway
- ABS.01.01: Apply micro- and macroeconomic principles to plan and manage inputs and outputs in an AFNR business.
- AFNR (Grades 9-12): Agribusiness Systems Career Pathway
- Social Studies – Economics
- Economics Standard 7 (Grades 9-12): Markets and Prices
- Objective (Grades 9-12): Identify markets in which they have participated as a buyer and as a seller and describe how the interaction of all buyers and sellers influences prices. Also, predict how prices change when there is either a shortage or surplus of the product available.
- Economics Standard 9 (Grades 9-12): Competition and Market Structure
- Objective (Grades 9-12): Explain how changes in the level of competition in different markets can affect price and output levels.
- Economics Standard 14 (Grades 9-12): Entrepreneurship
- Objective (Grades 9-12): Identify the risks and potential returns to entrepreneurship, as well as the skills necessary to engage in it. Understand the importance of entrepreneurship and innovation to economic growth, and how public policies affect incentives for and, consequently, the success of entrepreneurship in the United States.
- Economics Standard 7 (Grades 9-12): Markets and Prices
- Social Studies – Geography
- APHG Topic 5.1: Introduction to Agriculture
- PSO-5.A.2: Intensive farming practices include market gardening, plantation agriculture, and mixed crop/livestock systems.
- APHG Topic 5.6: Agricultural Production Regions
- PSO-5.C.1: Agricultural production regions are defined by the extent to which they reflect subsistence or commercial practices (monocropping or monoculture).
- APHG Topic 5.7: Spatial Organization of Agriculture
- PSO-5.C.3: Large-scale commercial agricultural operations are replacing small family farms.
- PSO-5.C.5: Technology has increased economies of scale in the agricultural sector and the carrying capacity of the land.
- APHG Topic 5.1: Introduction to Agriculture