Soybeans are Legumes
Soybeans are bushy green plants from the legume family. Scientifically speaking, legume plants have the ability to use soil bacteria to form a nodule on their roots by pulling nitrogen from the air and using this nutrient for growth. A simpler description of a legume is a plant that produces a seed that is contained in a pod. Examples of legumes grown in agriculture include soybeans, peas, and alfalfa. Legume crops are a natural benefit to soil quality on farms. The ability of legumes to “fix" their own nitrogen reduces the cost to farmers and gardeners for fertilizers and can be used in a crop rotation to replenish nitrogen in the soil. The fixating of nitrogen by soybeans also causes the seeds and pods to have very high protein contents.
Soybean Production
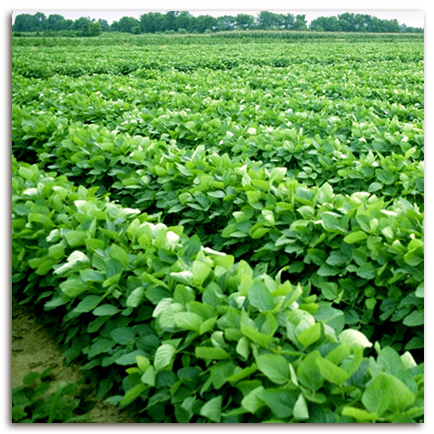

Soybeans are planted on farms in the spring after the last frost. After the seed germinates and begins to grow, it matures into a bushy, green plant which blooms in late summer. From these white or purple blossoms a pod begins to form. During the fall season, the soybeans mature, and the plant begins to turn yellow. The soybeans are harvested using a machine called a combine. The combine cuts the entire soybean plant and separates the soybeans from their pods and stems. The soybeans are then collected and trucked to facilities where they are stored and processed.
Seed Anatomy
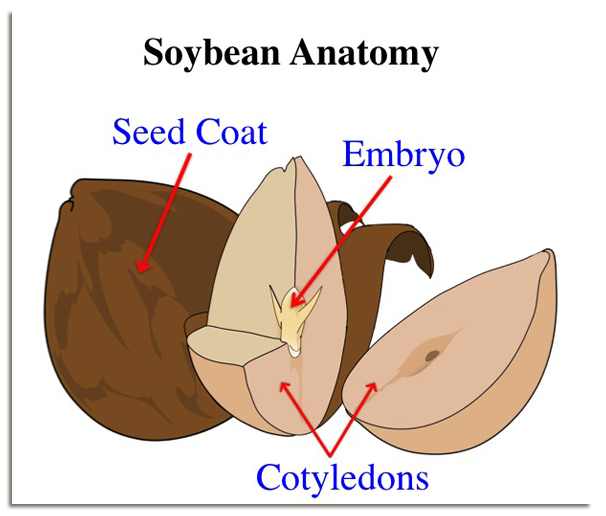
All members of the bean family (soybeans, lima beans, kidney beans, green beans, etc.) have the same seed anatomy. A seed coat is a very thin layer on the outer most surface of the seed. The seed coat offers protection to the cotyledons and the embryo. The cotyledons, or seed leaves, are the first leaves visible on a bean plant. These seed leaves are thick and contain stored glucose (food) for the new plant to grow. Before the seed is planted, the cotyledons are usually not green. When the plant sprouts, or germinates, chlorophyll is activated, and the cotyledons become green. The very center of a seed contains the embryo. This embryo is the new, or “baby,” plant that will sprout out of the soil. If bean seeds are soaked in water for a few hours, they can easily be pulled apart, and these major bean seed parts will be visible.
Soybean Uses
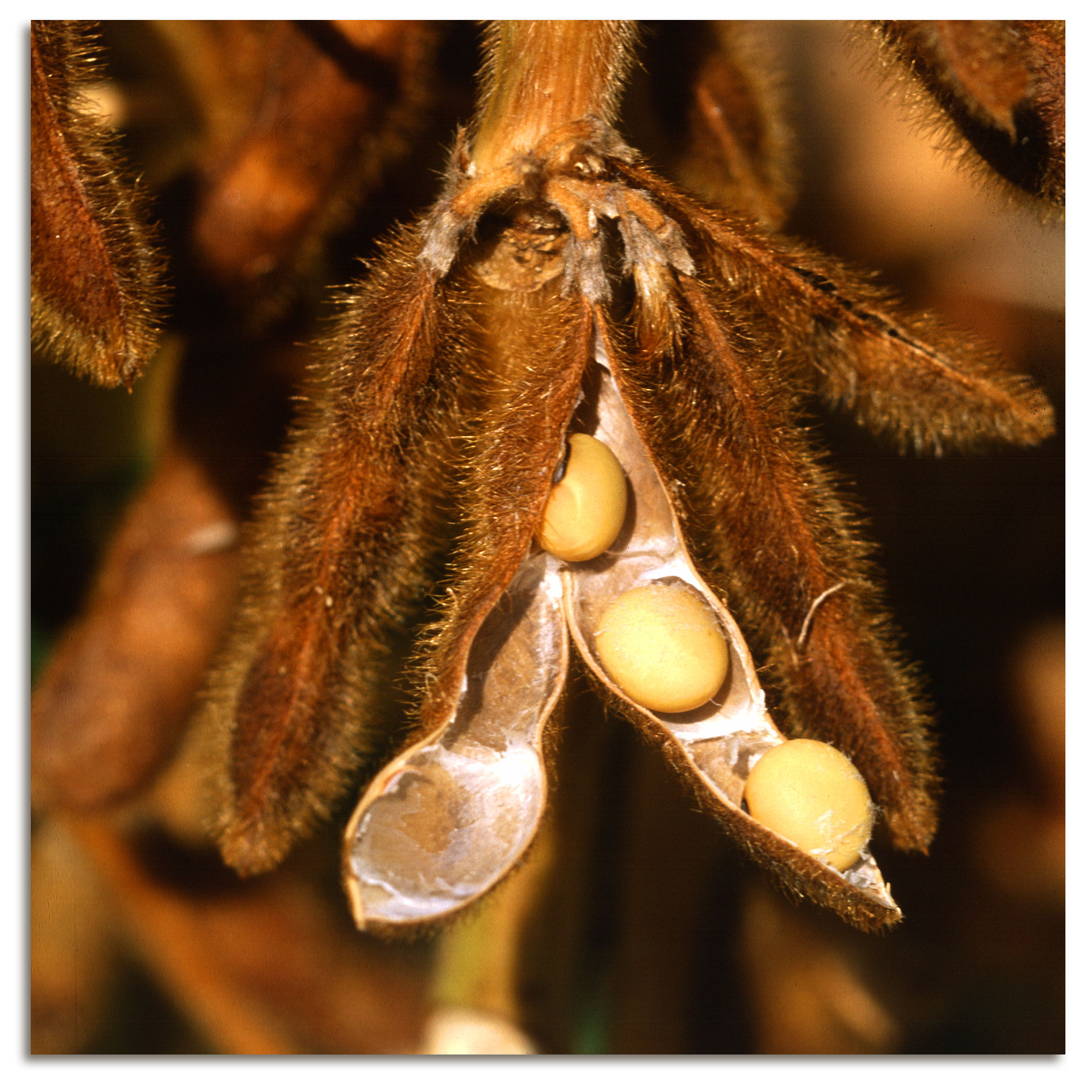

Soybeans are one of the most versatile crops in the world. When crushed and pressed, soybeans produce oil used in margarine, cooking oils, salad dressings, mayonnaise, and many prepared foods. Soybean oil contains no cholesterol and is low in saturated fat, so it is popular with health-conscious people. Soybean oil is also used to make paints, varnishes, soaps, cosmetics, plastics and crayons. Soybean oil is even used to make ink for printing newspapers and magazines. Soy biodiesel is another product made from soybean oil. This fuel is used in cars, trucks, and buses which reduces pollution and increases engine performance. After soybean oil is removed in processing, the remaining flakes are processed into food products or protein meal for animals. Soybean meal is an important protein source for livestock and poultry.
Edamame is an immature soybean harvested before it becomes dry and hardened. This variety of soybean is grown primarily for eating. These bright green soybeans can be purchased at the grocery store shelled or in the pod, fresh or frozen. The variety of soybean used for edamame typically has two or three beans per pod. In contrast, soybeans grown commercially for animal feed, oil, and other byproducts have three beans per pod.



