Food: Going the Distance
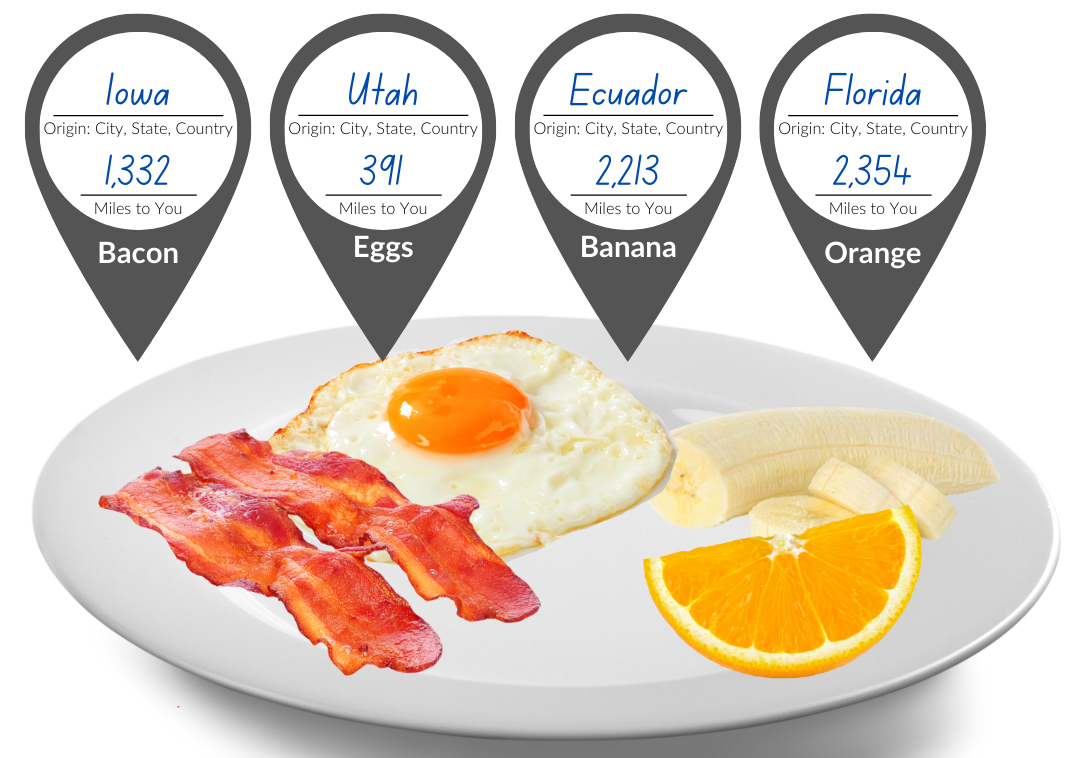
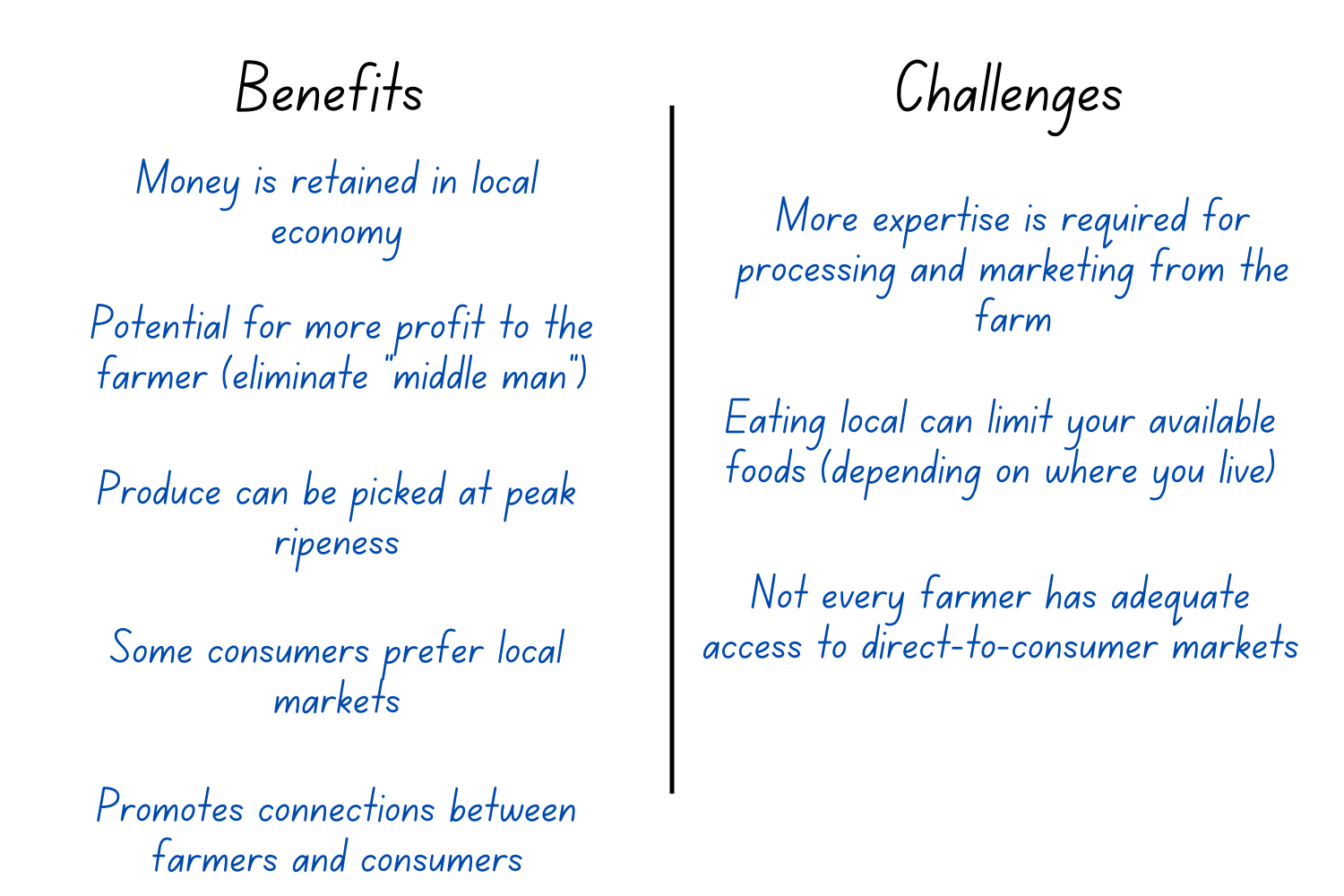
Students calculate the miles common food items travel from the farm to their plates and discuss the environmental, social, and economic pros and cons of eating local vs relying on a global marketplace for our food.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Andrea Gardner | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Sources
- How Far Does Your Food Travel to Get to Your Plate? | Foodwise
- The Facts About Food Miles | BBC Good Food
- Kay's Korner: The Food Waste Scandal | Western Livestock Journal
- Very Little of Global Food is Transported by Air | Our World in Data
- Food Miles | Sustainability: A Comprehensive Foundation
- Farms that Sell Directly to Consumers May Stay in Business Longer | USDA
- Why Buy Local? | Center for Community and Economic Development
- It's Time to Stop Comparing Meat Emissions to Flying | GHGGuru Blog
Standards
National Content Area Standards
- Career & Technical Education
- AFNR (Grades 9-12): Food Products and Processing Systems Career Pathway
- FPP.02.03: Apply principles of human behavior to develop food products to provide a safe, wholesome and nutritious food supply for local and global food systems.
- FPP.03.03: Create food distribution plans and procedures to ensure safe delivery of food products.
- AFNR (Grades 9-12): Food Products and Processing Systems Career Pathway
- Social Studies – Geography
- APHG Topic 5.8: Von Thünen Model
- PSO-5.D.1: Von Thünen’s model helps to explain rural land use by emphasizing the importance of transportation costs associated with distance from the market; however, regions of specialty farming do not always conform to von Thünen’s concentric rings.
- APHG Topic 5.11: Challenges of Contemporary Agriculture
- IMP-5.B.2: Patterns of food production and consumption are influenced by movements relating to individual food choice, such as urban farming, community-supported agriculture (CSA), organic farming, value-added specialty crops, fair trade, local-food movements, and dietary shifts.
- IMP-5.B.4: The location of food-processing facilities and markets, economies of scale, distribution systems, and government policies all have economic effects on food-production practices.
- APHG Topic 5.8: Von Thünen Model
- Science
- APES Unit 5: Land and Water Use
- EIN-2.M Impacts of Urbanization: Describe the effects of urbanization on the environment.
- EIN-2.N Ecological Footprints: Explain the variables measured in an ecological footprint.
- STB-1.E Sustainable Agriculture: Describe sustainable agricultural and food production practices.
- APES Unit 5: Land and Water Use