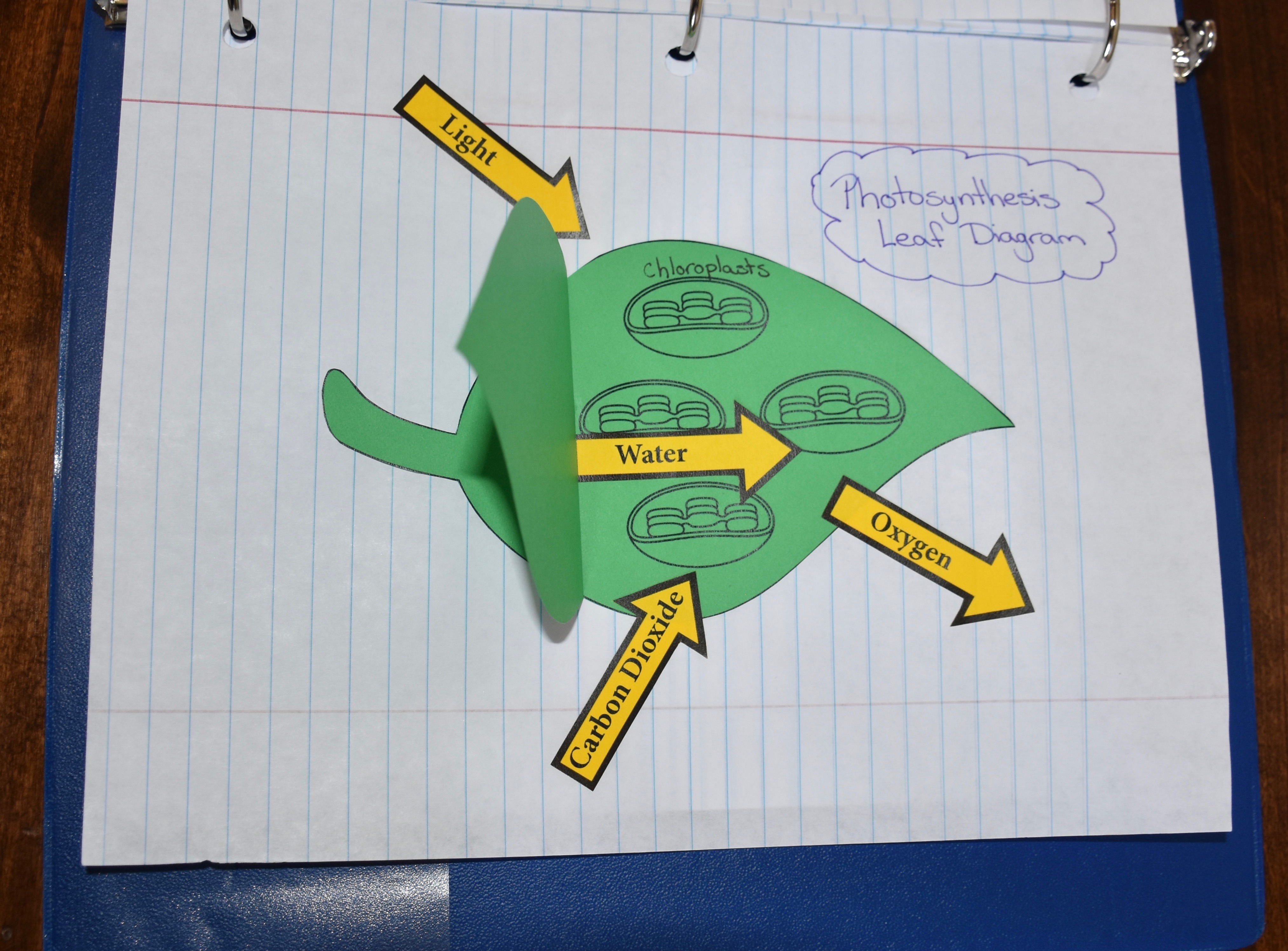
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy. Plants use the energy of light to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar (glucose) and oxygen. Carbon dioxide is absorbed by the leaves through the stomata. Water enters the plant at its roots and travels through the stem to reach the leaves. The leaves are the primary site where the photosynthesis process takes place. Inside the leaf cells are structures called chloroplasts. Each chloroplast contains chlorophyll, a chemical that gives leaves their green color. When the leaves receive light, chlorophyll captures the light's energy and stores it to eventually be used to convert water into hydrogen and oxygen. The water's hydrogen and oxygen atoms are combined with the carbon dioxide's carbon and oxygen atoms to create glucose molecules which are used by the plant to produce its food. Oxygen, a byproduct of the photosynthesis process, is released into the atmosphere through the stomata. In plants, photosynthesis only occurs in the presence of light.
Light requirements vary by plant species. Green plants need light to perform photosynthesis, although the intensity, quality, and duration needs will differ by plant. Understanding the light preferences of a plant is important when choosing an appropriate planting location and/or light source.
A grow light is an artificial light source designed to stimulate plant growth by emitting a light appropriate for photosynthesis.1 The purpose of a grow light is to replicate the natural solar spectrum of sunlight or to provide a light spectrum tailored to the needs of a particular plant. There are three main types of grow lights—fluorescent, LED (light-emitting diodes), and HID (high-intensity discharge).2 Grow lights differ from traditional light bulbs that are used to light homes. Unlike a traditional light bulb, grow lights produce the full spectrum of light and appropriate intensity necessary for photosynthesis. Grow lights also produce less heat than a traditional bulb, which prevents the scorching of plants.
Plants differ in their light intensity requirements. For grow lights, light intensity is determined by a bulb's brightness and the proximity of the light source to the plant. Plants native to tropical jungles or shady forests typically require less light as compared to plants from dry, sunny climates.
All plants need a rest from light. Respiration, an important part of a plant's growth process, occurs when it's dark. Botanists usually divide plants into three categories relating to their preferred day length—short-day plants grow best with less than 12 hours of light per day, long-day plants require 14-18 hours of light per day, and day neutral plants depend on 8-12 hours per day all year long.
There is a constant flow of energy in our world. This results in an energy supply chain which begins with the sun. Energy is transferred along this chain in different forms, which is important because all the living things require energy in specific forms. Energy helps organisms live and grow.
Plants use photosynthesis to capture light energy from the sun and convert it into food energy plants need to grow. This process requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water, which combine and convert to glucose and oxygen.3 Humans and animals use respiration to obtain energy by combining oxygen and glucose, which results in the release of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (cellular energy).
Cattle assist in the energy supply chain by converting energy that humans cannot use into energy that humans can use. Cattle have a four-compartment stomach which allow them to eat, digest, and use the energy from some parts of plants that humans cannot.5 This is the case with 75–80% of the feed dairy cows will eat.6 They eat byproducts like cotton seeds, almond hulls, distillers grain (leftover from processing cereal grains or beer), and sugar beet pulp.7 An animal nutritionist will help farmers decide exactly what goes into the feed to provide all the nutrients dairy cows need to grow and produce milk. Humans can then drink the milk the cows produce (or a variety of other dairy products) to get their own nutrition and energy. Dairy products provide a variety of nine essential nutrients, including all of the macronutrients (carbohydrates, fat, protein, and water). This makes dairy products an important part of a healthy diet for all age groups, and especially kids who are still growing.8
The movement of energy through the world is very important to keeping living things alive. It starts with the sun and plants through photosynthesis. Cows are then able to eat these plants (several that humans can't digest), use the energy to produce milk that humans can digest, and use the energy and nutrients to live and grow.