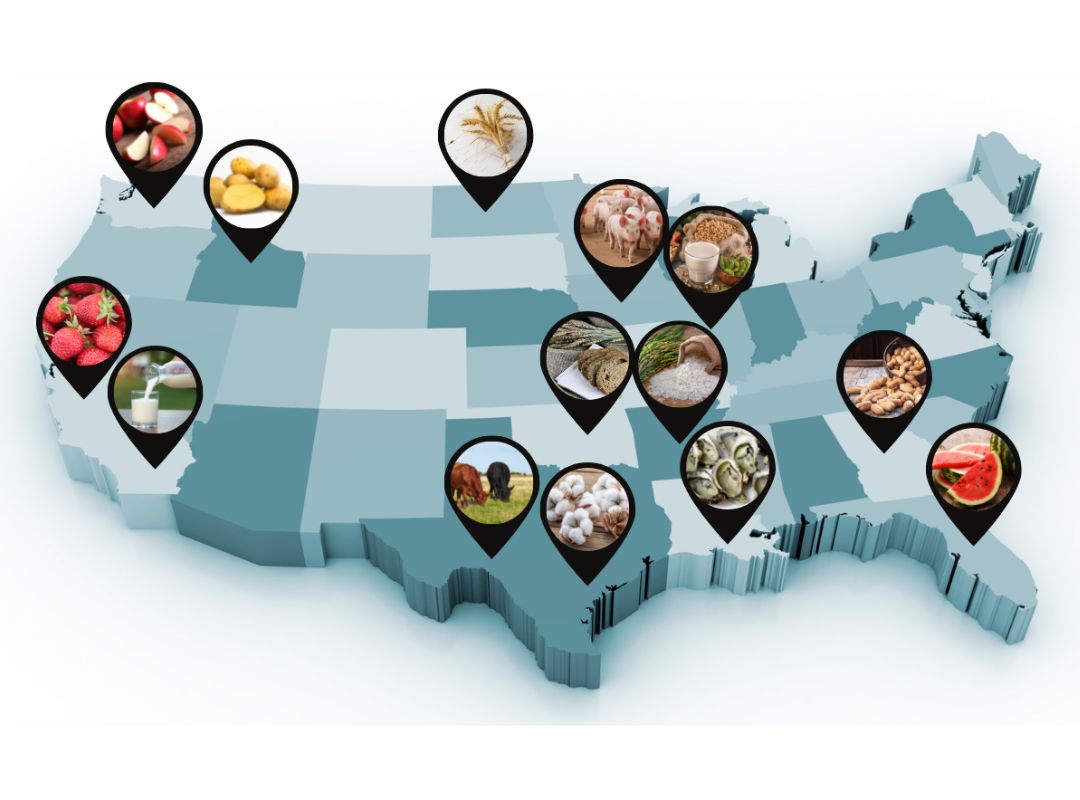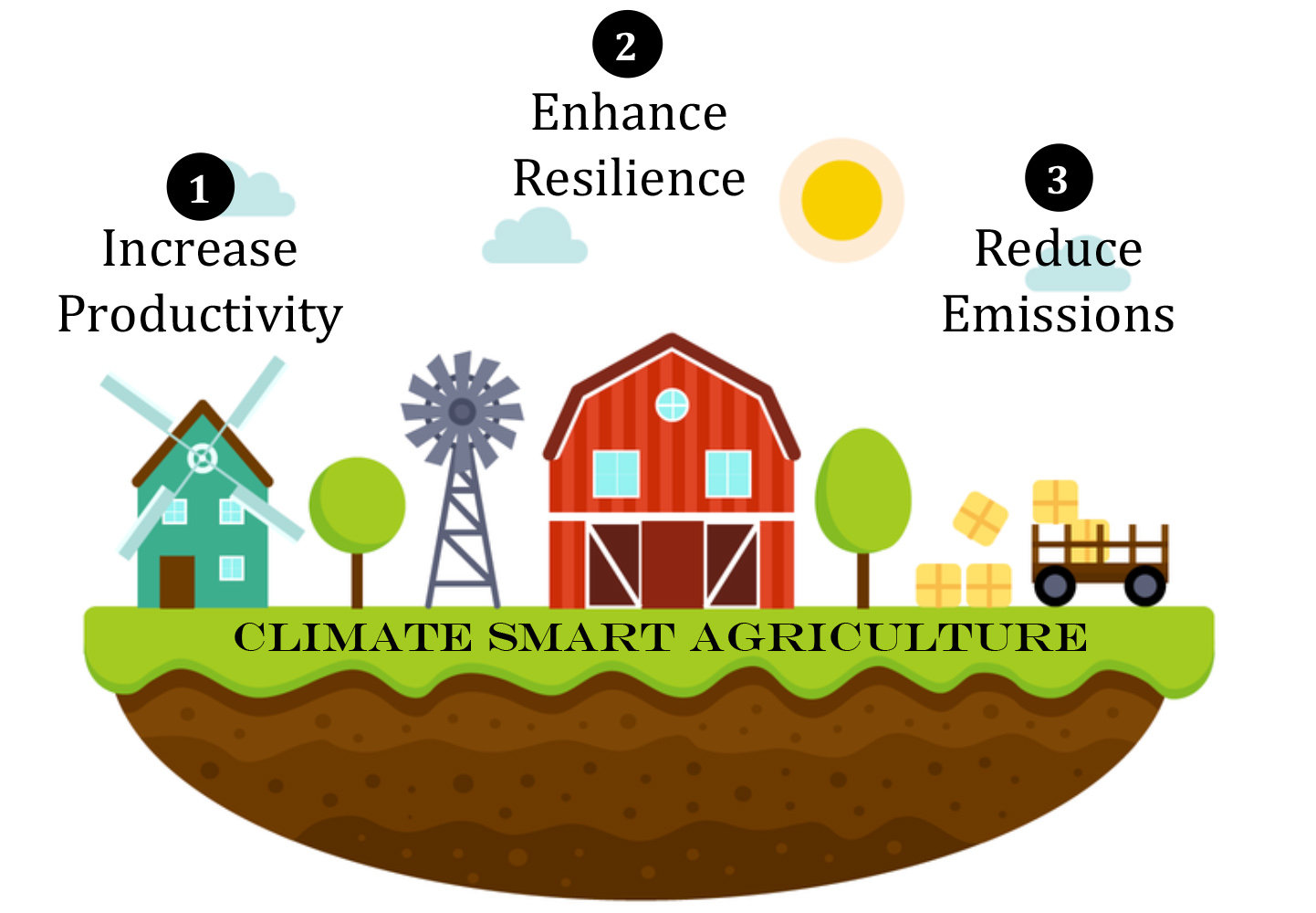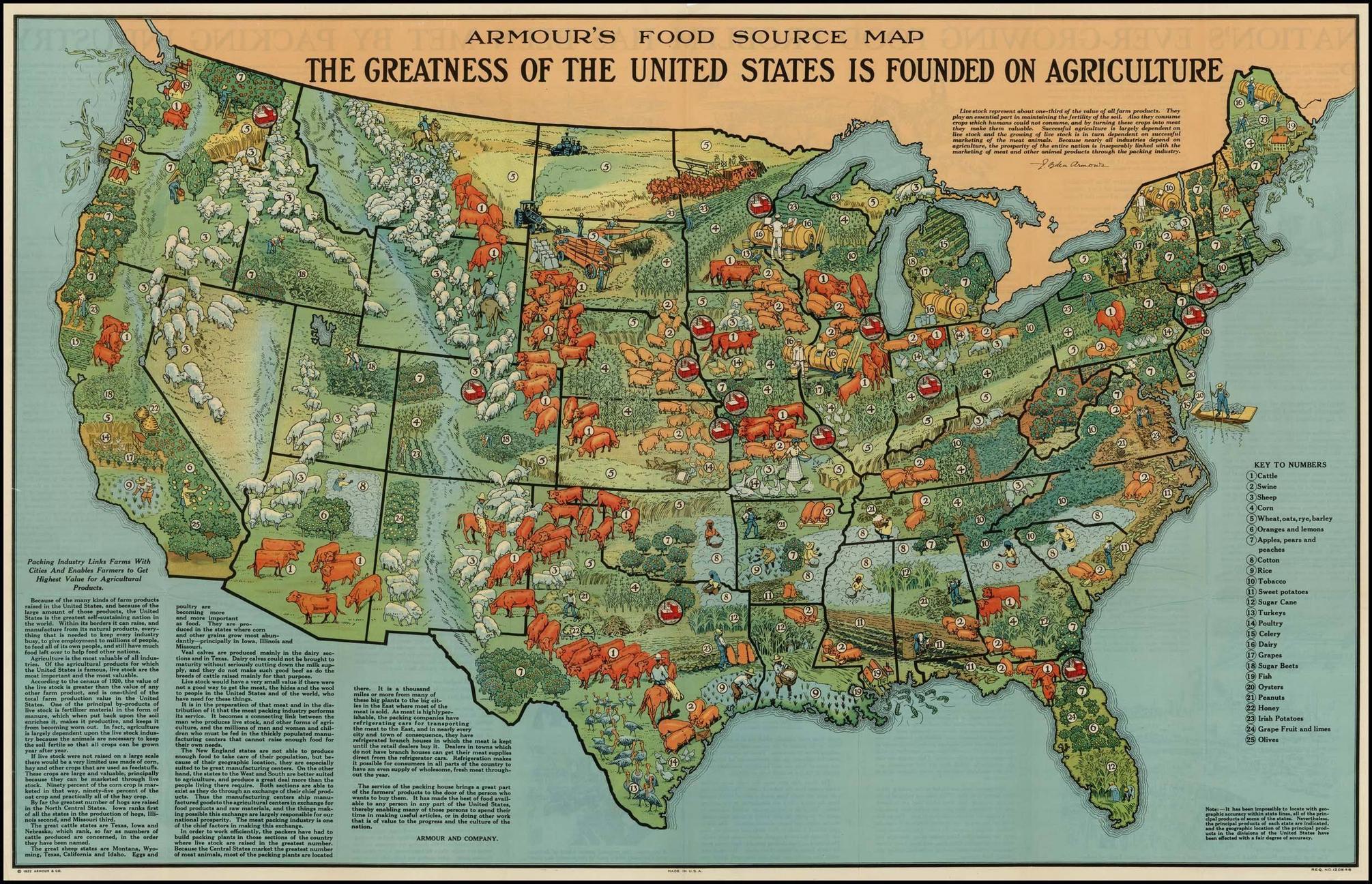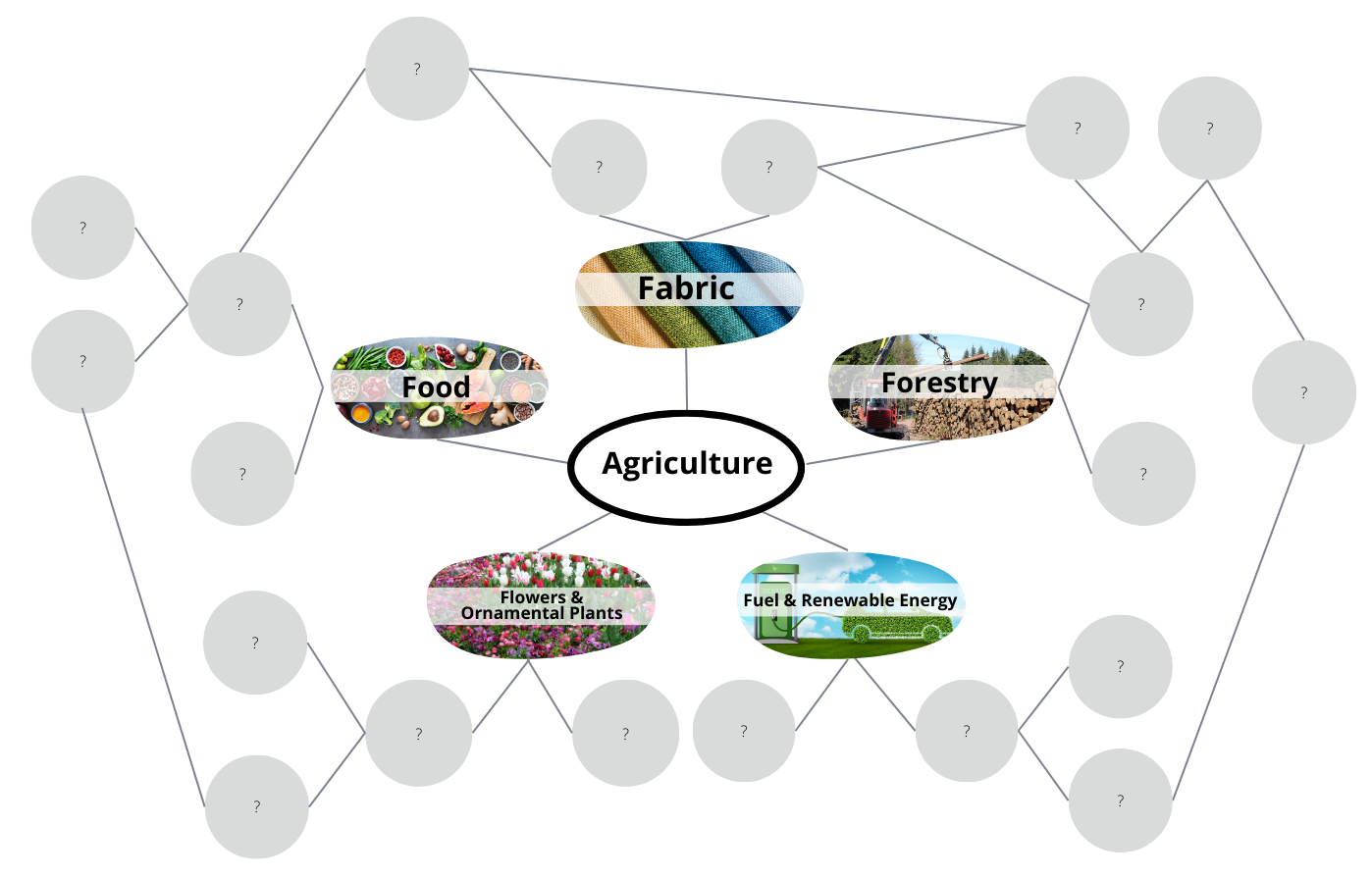
My Agricultural Connections (Grades 9-12)
Explore how we are each connected to agriculture through our food, clothing, shelter, fuel, and more. Students will be introduced to agriculture and begin to recognize the depth and complexities of agricultural systems locally and globally.