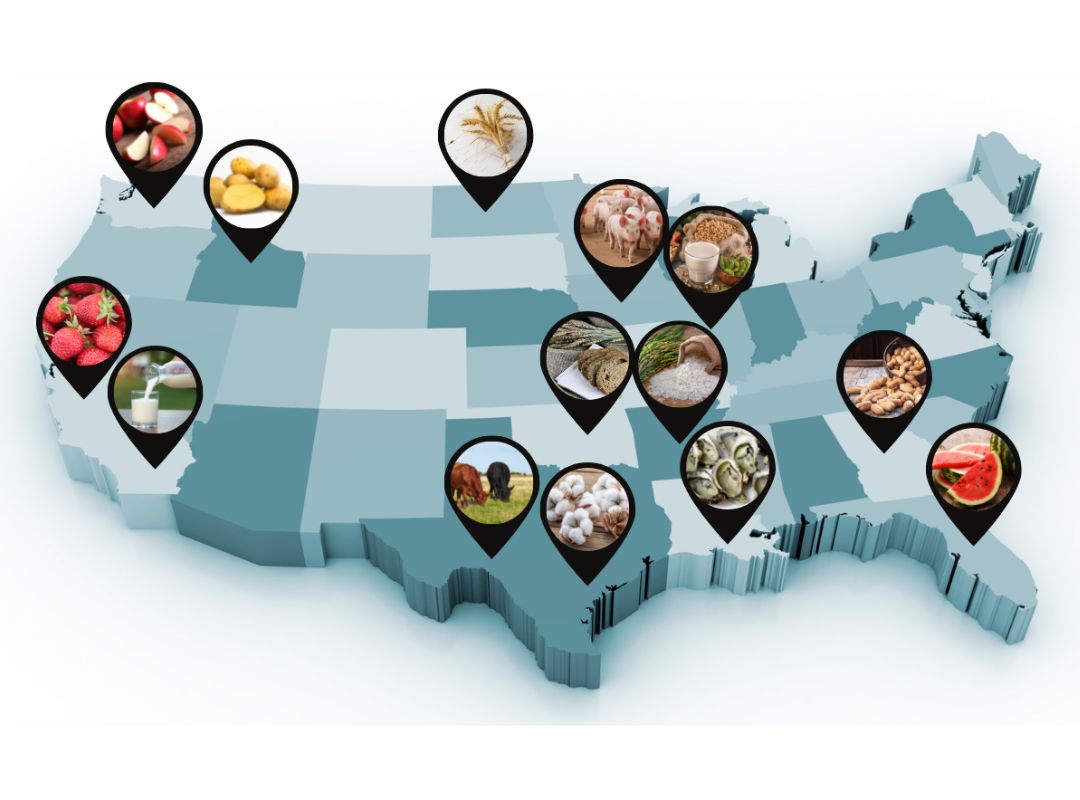
Geography and Climate for Agricultural Landscapes (Grades 6-8)
Students will discover how geography and climate influence the crops that are grown and the livestock that is raised in each state.

Students will discover how geography and climate influence the crops that are grown and the livestock that is raised in each state.
Students will explore the path food takes along the Farm-to-Table Continuum. They will begin on the farm and investigate food safety issues during processing, transportation, at restaurants and supermarkets, and finally, in their own homes. Teams will identify how food can become contaminated along the continuum and develop and present strategies for preventing contamination at each step.
In this activity, students will develop an awareness of the importance of food safety in retail food establishments. They will be challenged to design and manage their own food-safe supermarket department using the 4 Cs of Food Safety. At the end of this activity, each team will present its findings in an innovative presentation.
This lab challenges students to identify the variables involved in handwashing. They will design labs to discover the best method for washing their hands to reduce the spread of bacteria. Students will also analyze and present the data.

Students will understand water-based state changes that occur at varying temperatures, recognize the importance of the proper hand washing technique for general health and disease prevention, understand the factors that impact mold growth and their application to food safety, and explore ways to prevent foodborne illness.
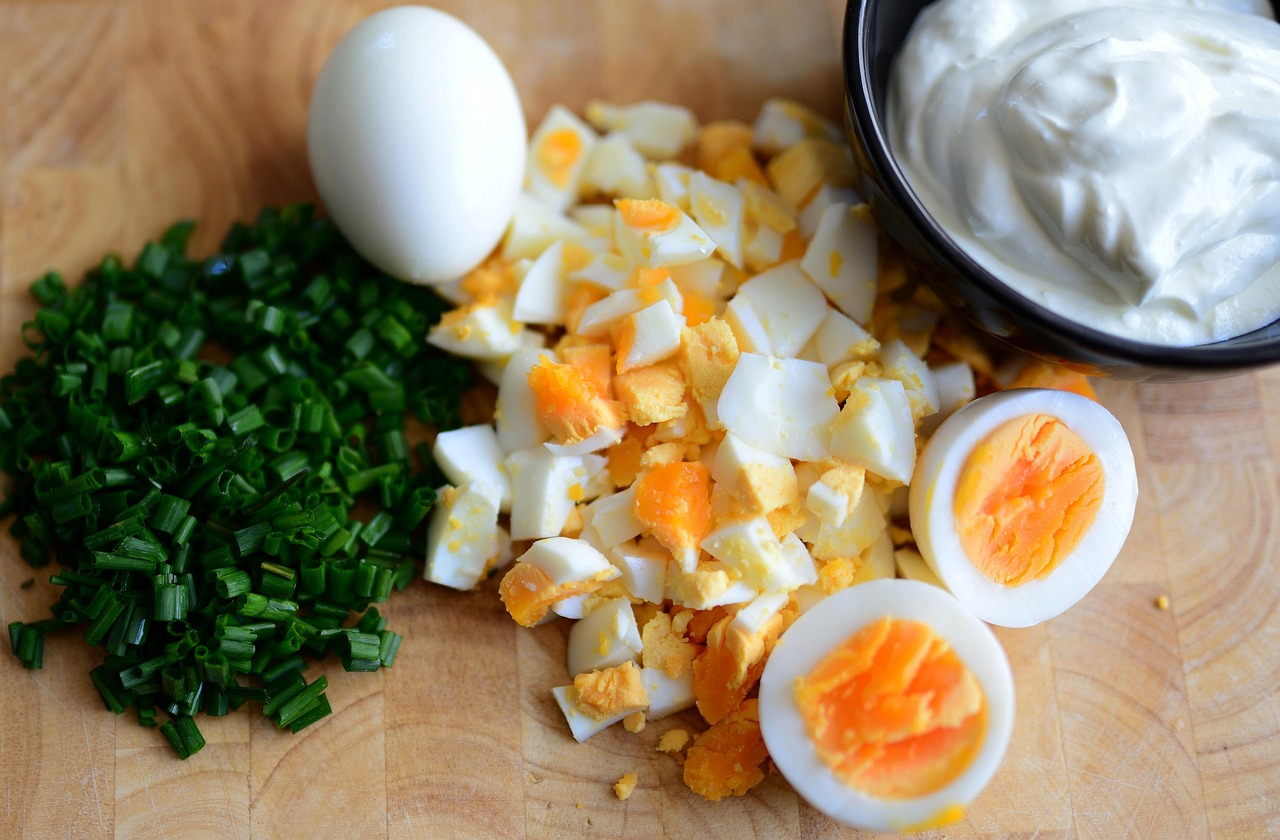

Students will learn the versatility, function, and nutritional benefit of eggs in a healthy diet, identify the function and role of eggs in a recipe, identify forms of technology used on an egg farm, and understand how eggs are classified by size.
Students will discover that some items in their own kitchens may be contaminated by bacteria. They will be challenged to hypothesize about where bacteria might be found in kitchens and which items might have the most and the least bacteria. Students will develop awareness that bacteria can spread from surfaces to hands, and even to food, and will hypothesize how to control the spread of bacteria.
Students will explore the varied roles that microorganisms play in the world as well as different methods for controlling their growth. Activities include using a dichotomous key to identify waterborne diseases, comparing effectiveness of handwashing techniques, reading fictional and factual excerpts about microbes, and experimenting with the growth of microorganisms on potato slices.
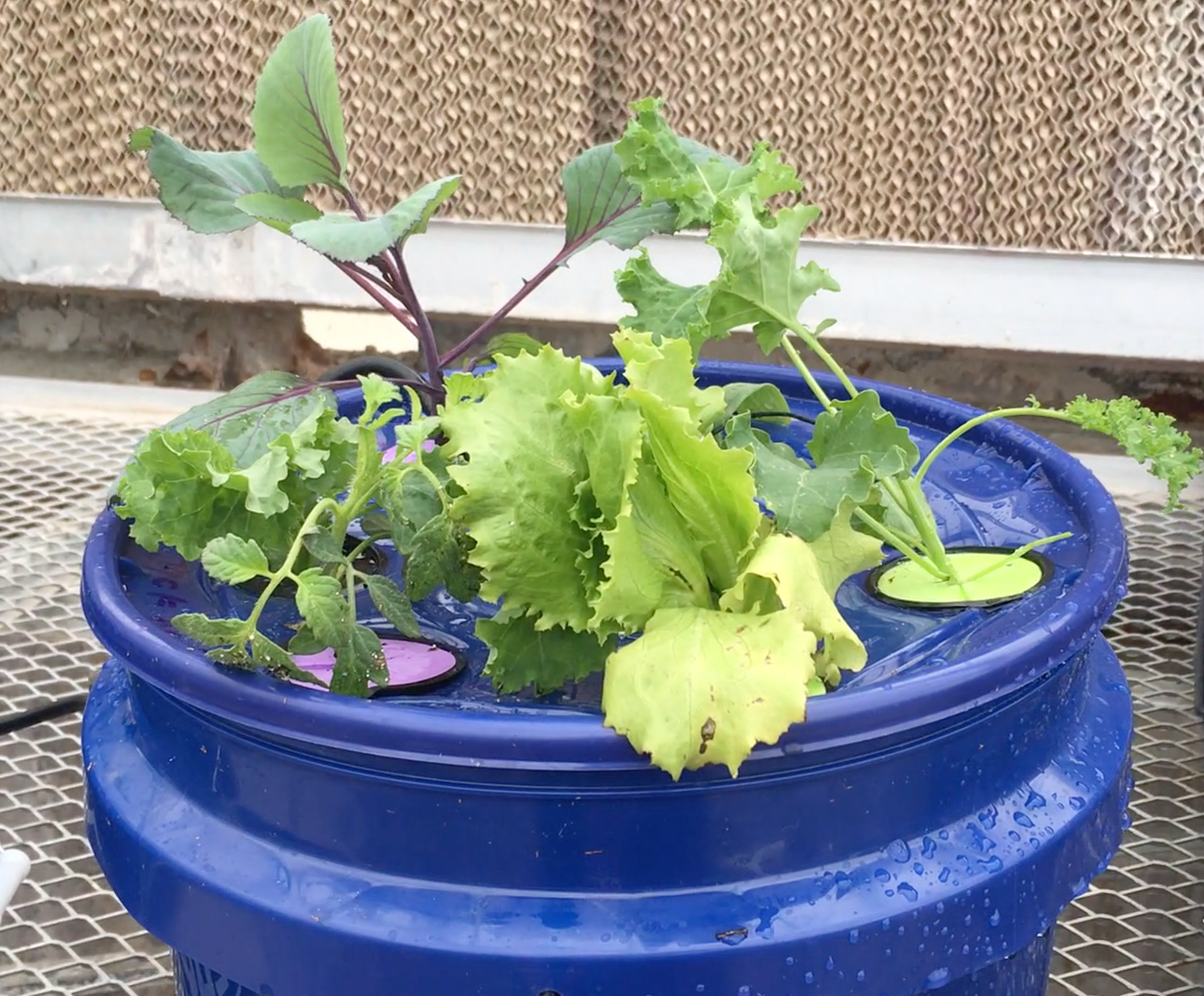

Students will use the Engineering Design Process to develop and construct an aeroponic garden to grow a food crop. Students will develop and apply an understanding of plant anatomy and physiology related to plant growth and ultimately discuss the possibilities and limitations of using vertical farming to produce our food.
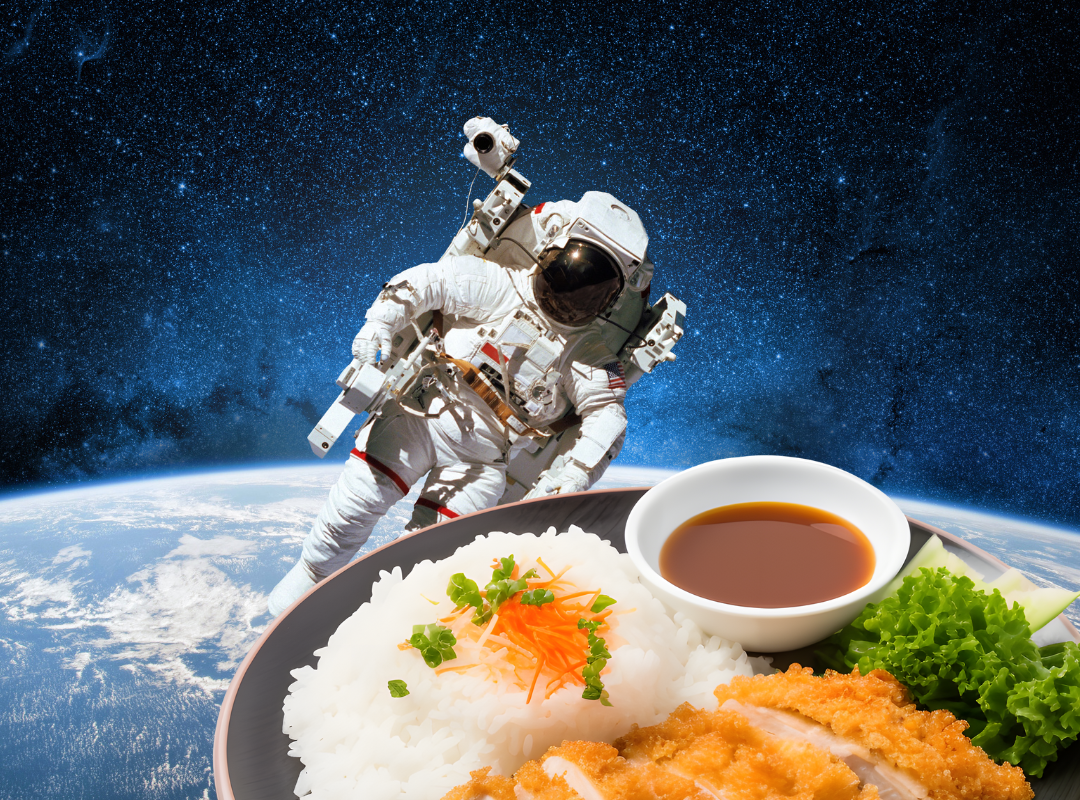

Through project-based learning, students work in groups to create a flavorful and nutritious meal for astronauts to eat in space. They experience careers in food and nutrition, food science, and marketing, research different ways to preserve foods, and discover how food is taken to and eaten in space.
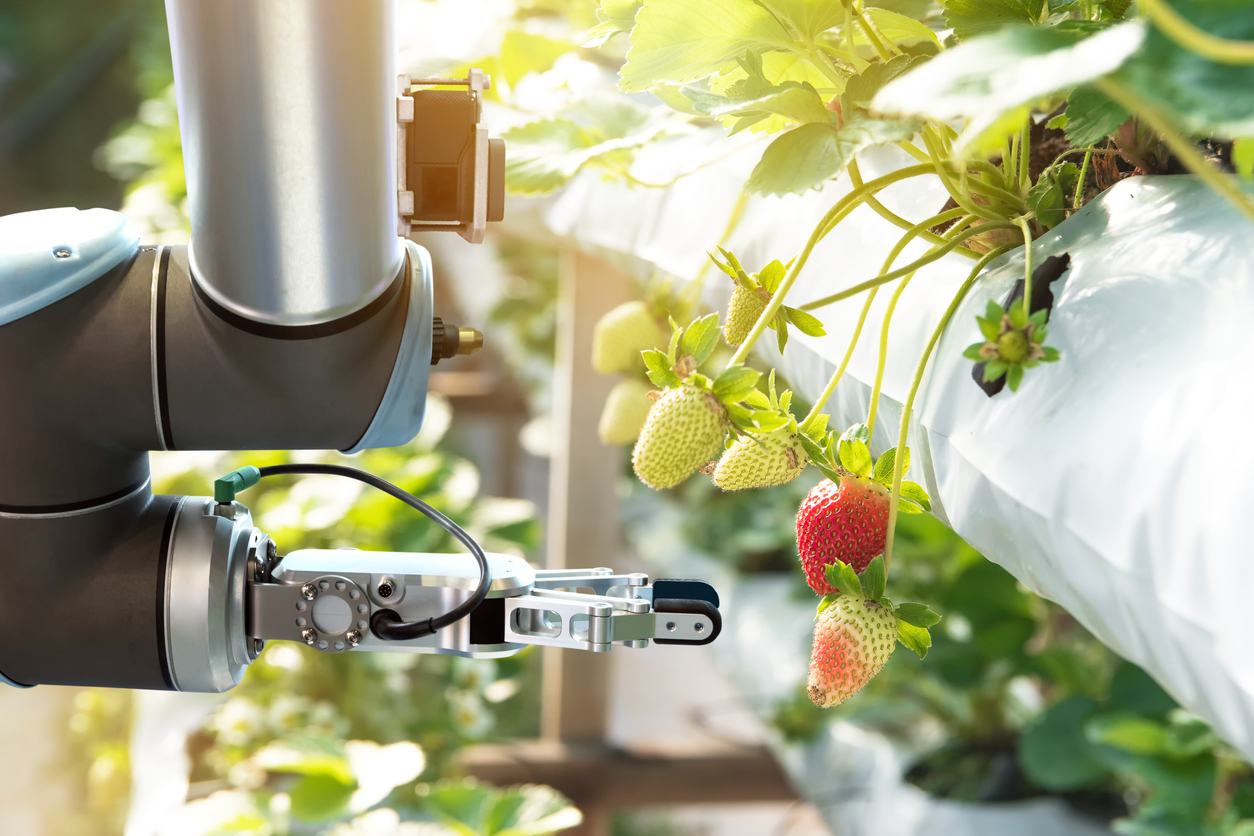

Through project-based learning, students examine fruit and vegetable farms to discover the amount of manual labor required to plant, grow, and harvest some of our food. They research the business economics of farm management, the plant life cycle, and the requirements and challenges faced in reducing manual labor through mechanization or robotics. Students present their findings to an agricultural engineer to begin developing a solution to farm labor shortages.

Through project-based learning, students solve the problem of excess beeswax, a byproduct of honey bees, by developing a useful beeswax product and marketing their product to be sold in a local boutique or farmers market.