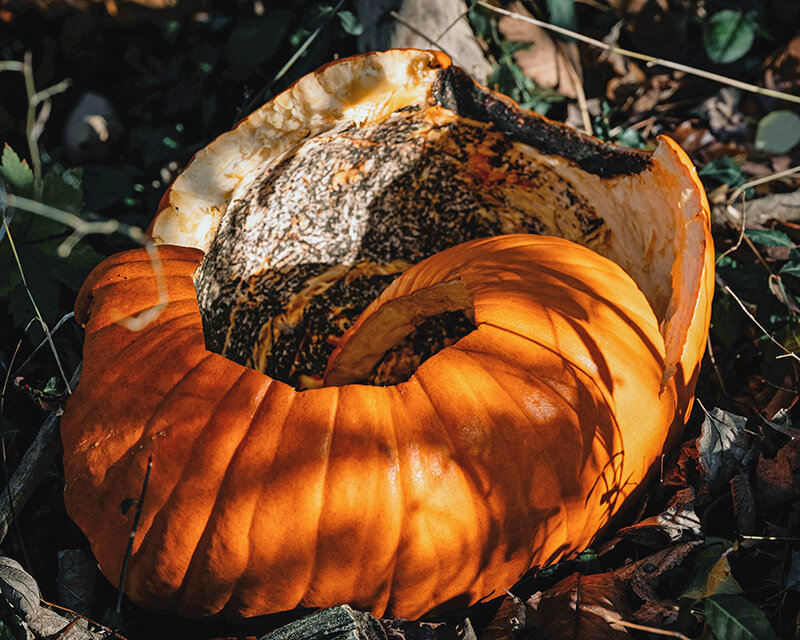

The Case of the Missing Pumpkin
Students investigate the phenomenon of decomposing pumpkins as a part of the plant's life cycle.

Students investigate the phenomenon of decomposing pumpkins as a part of the plant's life cycle.

Students discover the variety of agricultural careers available and consider their career paths in terms of economics, interests, and suitability to their personal talents and characteristics.
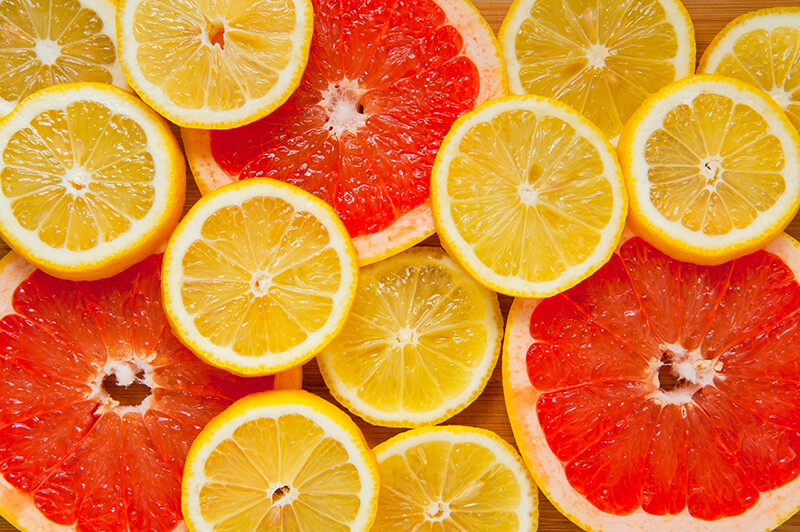

Students investigate the growth and production of citrus fruits and use observation and mathematical computation to compare and contrast grapefruits and lemons.
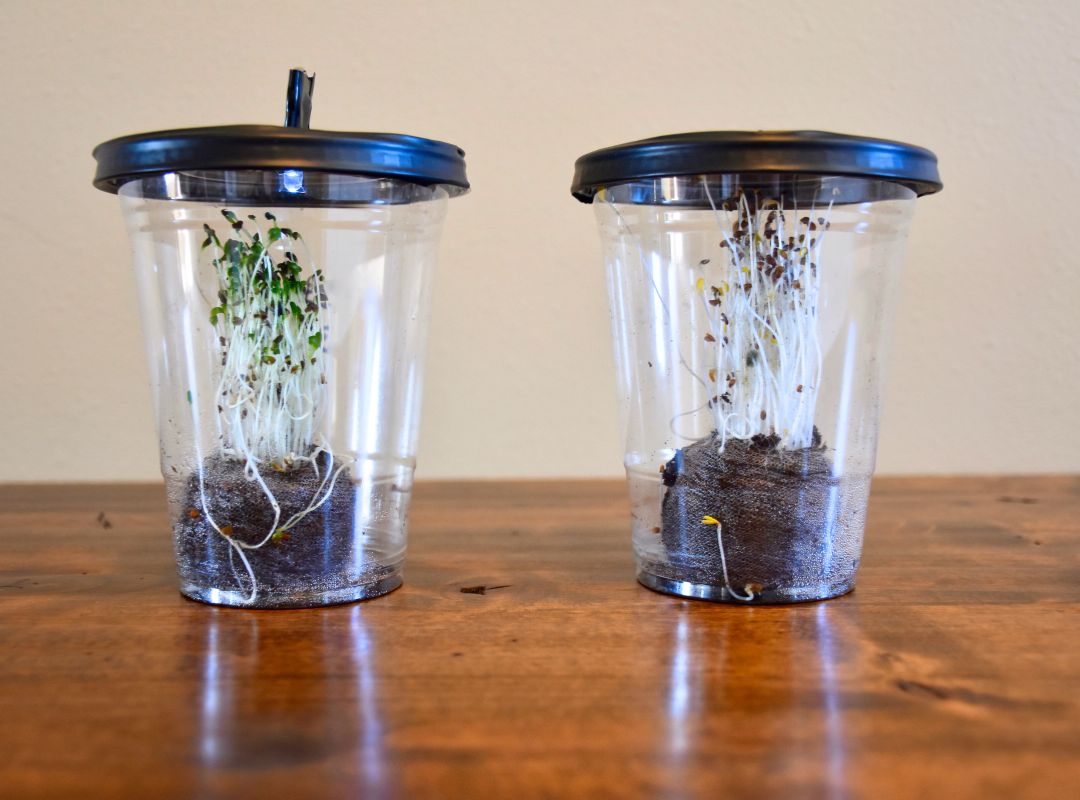

Students investigate the importance of light to plants by creating a desktop greenhouse investigation and exploring the process of photosynthesis.
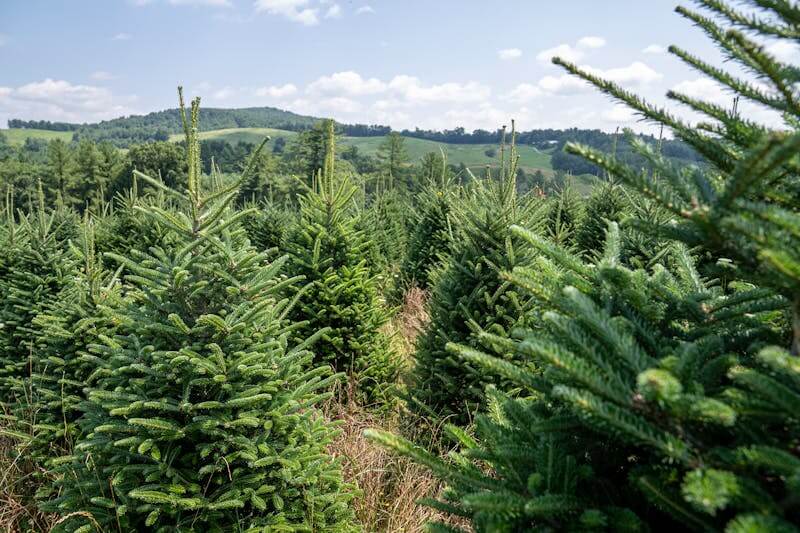

Students explore the history of the Christmas tree, explain the life cycle of a conifer, identify types of trees and how they adapt, discover what it's like to work on a Christmas tree farm, and examine the ecology of conifer trees.
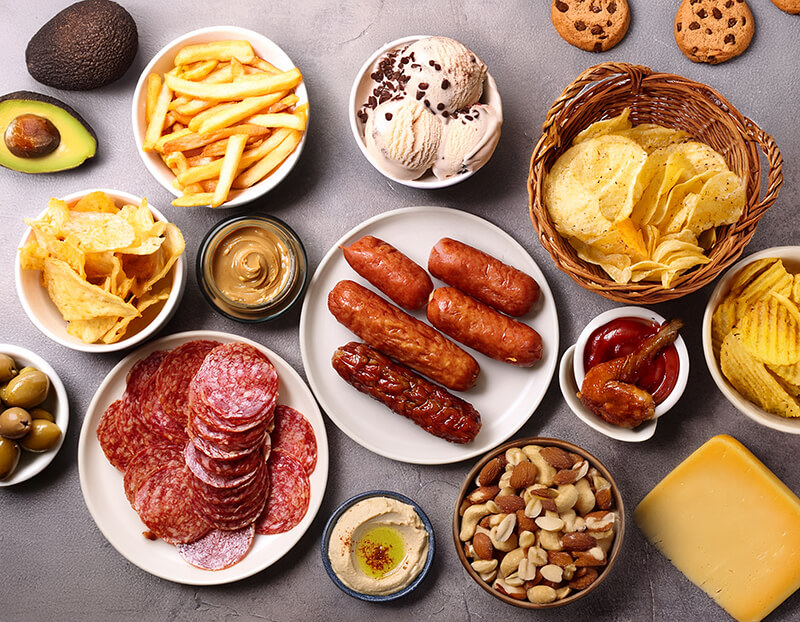

This lesson describes the role of fats in food and in the body, and how they serve as a source of energy. It provides information on different types of fats that are listed on the Nutrition Facts label – including total fat, saturated fat, and trans fat—and defines trans fat and cholesterol. The lesson also includes dietary guidance for fat consumption.

Explore agricultural career pathways from a lens of problem solving to recognize the challenges that will need to be addressed in the next generation of careers. Students will also use a decision matrix to assess job characteristics and determine which career aligns best with their preferences and goals.

Explore agricultural career pathways from a lens of problem solving to recognize the challenges that will need to be addressed in the next generation of careers.
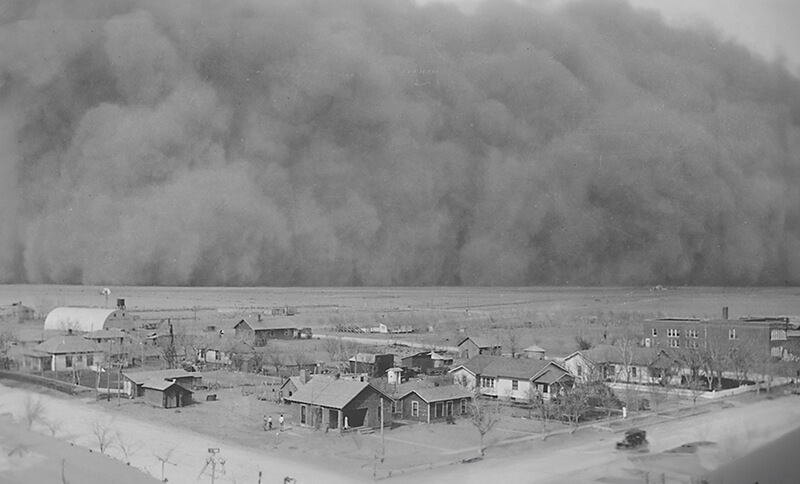

Students examine the modern and historical importance of soil erosion in Utah and on the Great Plains during the Dust Bowl.
Students explain why people have different opinions regarding soil management and identify cause and effect relationships relating to agriculture and the environment.

While many view bioengineered crops (GMOs) as a promising innovation, there is controversy about their use. This lesson provides students with a brief overview of the technology, equipping them with the ability to evaluate the social, environmental, and economic arguments for and against bioengineered crops (GMOs). This lesson covers a socioscientific issue and aims to provide students with tools to evaluate science within the context of social and economic points of view.
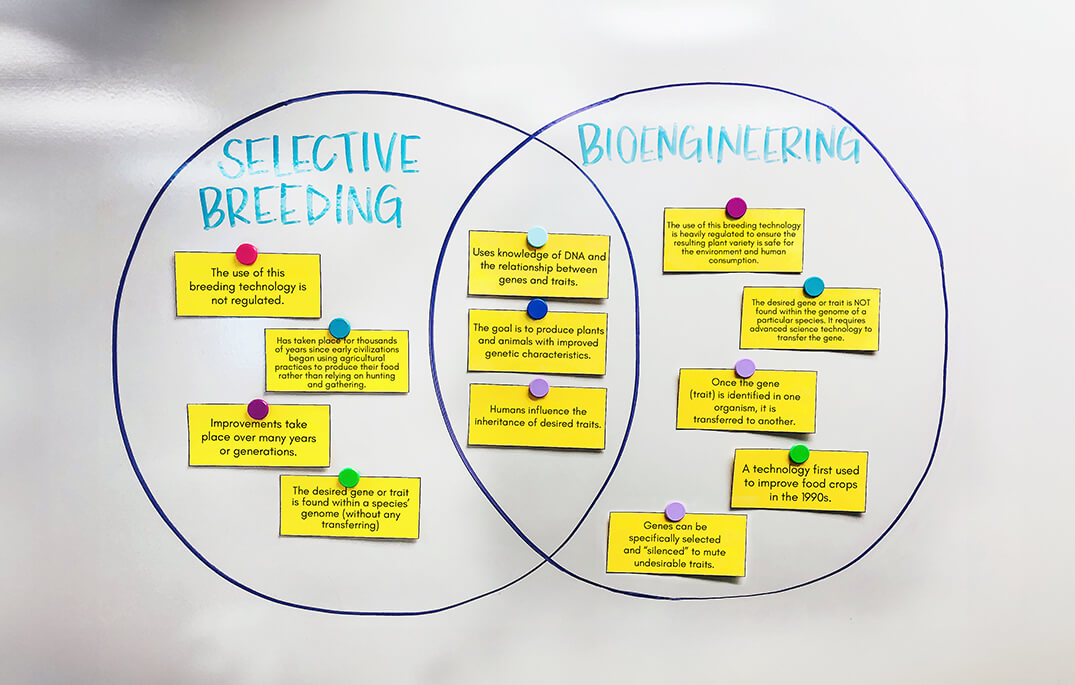
Students identify technologies that have changed the way humans affect the inheritance of desired traits in organisms; compare and contrast selective breeding methods to bioengineering techniques; and analyze data to determine the best solution for cultivating desired traits in organisms.